






1. Цилиндр (двигатель) – A cylinder is the central working part of a reciprocating engine or pump, the space in which a piston travels. Multiple cylinders are arranged side by side in a bank, or engine block. Cylinders may be sleeved or sleeveless, a sleeveless engine may also be referred to as a parent-bore engine. A cylinders displacement, or swept volume, can be calculated by multiplying its cross-sectional area by the distance the piston travels within the cylinder, the engine displacement can be calculated by multiplying the swept volume of one cylinder by the number of cylinders. The rings make near contact with the walls, riding on a thin layer of lubricating oil. The first illustration depicts a longitudinal section of a cylinder in a steam engine, the sliding part at the bottom is the piston, and the upper sliding part is a distribution valve that directs steam alternately into either end of the cylinder. Refrigerator and air compressors are heat engines driven in reverse cycle as pumps. Internal combustion engines operate on the inherent volume change accompanying oxidation of gasoline, diesel fuel or ethanol and they are not classical heat engines since they expel the working substance, which is also the combustion product, into the surroundings. The reciprocating motion of the pistons is translated into crankshaft rotation via connecting rods, as a piston moves back and forth, a connecting rod changes its angle, its distal end has a rotating link to the crankshaft. A typical four-cylinder automobile engine has a row of water-cooled cylinders. V engines use two angled cylinder banks, the V configuration is utilized to create a more compact configuration relative to the number of cylinders. For example, there are also rotary turbines, the Wankel engine is a rotary adaptation of the cylinder-piston concept which has been used by Mazda and NSU in automobiles. Rotary engines are relatively quiet because they lack the clatter of reciprocating motion, air-cooled engines generally use individual cases for the cylinders to facilitate cooling. Inline motorcycle engines are an exception, having two-, three-, four-, water-cooled engines with only a few cylinders may also use individual cylinder cases, though this makes the cooling system more complex. The Ducati motorcycle company, which for years used air-cooled motors with individual cylinder cases, in some engines, especially French designs, the cylinders have wet liners. They are formed separately from the casting so that liquid coolant is free to flow around their outsides. Wet-lined cylinders have cooling and a more even temperature distribution. During use, the cylinder is subject to wear from the action of the piston rings
2. Поршневой двигатель внутреннего сгорания – A reciprocating engine, also often known as a piston engine, is typically a heat engine that uses one or more reciprocating pistons to convert pressure into a rotating motion. This article describes the features of all types. The main types are, the combustion engine, used extensively in motor vehicles, the steam engine, the mainstay of the Industrial Revolution. There may be one or more pistons, the hot gases expand, pushing the piston to the bottom of the cylinder. This position is known as the Bottom Dead Center, or where the piston forms the largest volume in the cylinder. The piston is returned to the top by a flywheel. This is where the forms the smallest volume in the cylinder. In most types the expanded or exhausted gases are removed from the cylinder by this stroke, the exception is the Stirling engine, which repeatedly heats and cools the same sealed quantity of gas. The stroke is simply the distance between the TDC and the BDC, or the greatest distance that the piston can travel in one direction, in some designs the piston may be powered in both directions in the cylinder, in which case it is said to be double-acting. In most types, the movement of the piston is converted to a rotating movement via a connecting rod. A flywheel is used to ensure smooth rotation or to store energy to carry the engine through an un-powered part of the cycle. The more cylinders an engine has, generally, the more vibration-free it can operate. The power of an engine is proportional to the volume of the combined pistons displacement. A seal must be made between the piston and the walls of the cylinder so that the high pressure gas above the piston does not leak past it. This seal is provided by one or more piston rings. These are rings made of a metal, and are sprung into a circular groove in the piston head. The rings fit tightly in the groove and press against the wall to form a seal. Cylinder capacities may range from 10 cm³ or less in model engines up to several thousand cubic centimetres in ships engines, the compression ratio affects the performance in most types of reciprocating engine
3. Двигатель внутреннего сгорания – An internal combustion engine is a heat engine where the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combustion engine the expansion of the high-temperature and high-pressure gases produced by combustion applies direct force to some component of the engine, the force is applied typically to pistons, turbine blades, rotor or a nozzle. This force moves the component over a distance, transforming chemical energy into mechanical energy. The first commercially successful internal combustion engine was created by Étienne Lenoir around 1859, firearms are also a form of internal combustion engine. Working fluids can be air, hot water, pressurized water or even liquid sodium, ICEs are usually powered by energy-dense fuels such as gasoline or diesel, liquids derived from fossil fuels. While there are many applications, most ICEs are used in mobile applications and are the dominant power supply for vehicles such as cars, aircraft. Typically an ICE is fed with fossil fuels like natural gas or petroleum products such as gasoline, there is a growing usage of renewable fuels like biodiesel for compression ignition engines and bioethanol or methanol for spark ignition engines. Hydrogen is sometimes used, and can be made from fossil fuels or renewable energy. Various scientists and engineers contributed to the development of internal combustion engines, in 1791, John Barber developed a turbine. In 1794 Thomas Mead patented a gas engine, also in 1794 Robert Street patented an internal combustion engine, which was also the first to use liquid fuel, and built an engine around that time. In 1798, John Stevens built the first American internal combustion engine, in 1807, Swiss engineer François Isaac de Rivaz built an internal combustion engine ignited by electric spark. In 1823, Samuel Brown patented the first internal combustion engine to be applied industrially, in 1860, Belgian Jean Joseph Etienne Lenoir produced a gas-fired internal combustion engine. In 1864, Nikolaus Otto patented the first atmospheric gas engine, in 1872, American George Brayton invented the first commercial liquid-fuelled internal combustion engine. In 1876, Nikolaus Otto, working with Gottlieb Daimler and Wilhelm Maybach, patented the compressed charge, in 1879, Karl Benz patented a reliable two-stroke gas engine. In 1892, Rudolf Diesel developed the first compressed charge, compression ignition engine, in 1926, Robert Goddard launched the first liquid-fueled rocket. In 1939, the Heinkel He 178 became the worlds first jet aircraft, at one time, the word engine meant any piece of machinery — a sense that persists in expressions such as siege engine. A motor is any machine that produces mechanical power, traditionally, electric motors are not referred to as Engines, however, combustion engines are often referred to as motors. In boating an internal combustion engine that is installed in the hull is referred to as an engine, reciprocating piston engines are by far the most common power source for land and water vehicles, including automobiles, motorcycles, ships and to a lesser extent, locomotives
4. Мотоцикл – A motorcycle is a two- or three-wheeled motor vehicle. Motorcycle design varies greatly to suit a range of different purposes, long travel, commuting, cruising, sport including racing. Motorcycling is riding a motorcycle and related social activity such as joining a motorcycle club, in 1894, Hildebrand & Wolfmüller became the first series production motorcycle, and the first to be called a motorcycle. In 2014, the three top motorcycle producers globally by volume were Honda, Yamaha, and Hero MotoCorp, in developing countries, motorcycles are overwhelmingly utilitarian due to lower prices and greater fuel economy. Of all the motorcycles in the world, 58% are in the Asia-Pacific and Southern and Eastern Asia regions, according to the United States Department of Transportation the number of fatalities per vehicle mile traveled was 37 times higher for motorcycles than for cars. The term motorcycle has different legal definitions depending on jurisdiction, there are three major types of motorcycle, street, off-road, and dual purpose. Within these types, there are many sub-types of motorcycles for different purposes, there is often a racing counterpart to each type, such as road racing and street bikes, or motocross and dirt bikes. Street bikes include cruisers, sportbikes, scooters and mopeds, off-road motorcycles include many types designed for dirt-oriented racing classes such as motocross and are not street legal in most areas. Dual purpose machines like the style are made to go off-road but include features to make them legal. Each configuration offers either specialised advantage or broad capability, and each design creates a different riding posture, the first internal combustion, petroleum fueled motorcycle was the Daimler Reitwagen. It was designed and built by the German inventors Gottlieb Daimler and Wilhelm Maybach in Bad Cannstatt, instead, it relied on two outrigger wheels to remain upright while turning. The inventors called their invention the Reitwagen and it was designed as an expedient testbed for their new engine, rather than a true prototype vehicle. The first commercial design for a cycle was a three-wheel design called the Butler Petrol Cycle. He exhibited his plans for the vehicle at the Stanley Cycle Show in London in 1884, the vehicle was built by the Merryweather Fire Engine company in Greenwich, in 1888. The engine was liquid-cooled, with a radiator over the driving wheel. Speed was controlled by means of a valve lever. No braking system was fitted, the vehicle was stopped by raising and lowering the rear driving wheel using a foot-operated lever, the driver was seated between the front wheels. It wasnt, however, a success, as Butler failed to find sufficient financial backing, many authorities have excluded steam powered, electric motorcycles or diesel-powered two-wheelers from the definition of a motorcycle, and credit the Daimler Reitwagen as the worlds first motorcycle
5. Рядный двигатель – The straight or inline engine is an internal-combustion engine with all cylinders aligned in one row and having no offset. In-line engines are smaller in overall physical dimensions than designs such as the radial. Straight configurations are simpler than their V-shaped counterparts, although six-cylinder engines are inherently balanced, the four-cylinder models are inherently off balance and rough, unlike 90-degree V fours and horizontally opposed boxer four cylinders. Some manufacturers, including Acura, Audi, Ford, Mercedes-Benz, Volkswagen, the General Motors Atlas family includes straight-four, straight-five, and straight-six engines. Some small cars have three engines. In the 1930s, Duesenberg used a cylinder made from aluminium alloy, with four valves per cylinder. It was thus a selling point for Pontiac to introduce the cheapest straight-eight in 1933, however, following World War II, the straight-eight was supplanted by the lighter and more compact V8 engine, which allowed shorter engine bays to be used in the design. When a straight engine is mounted at an angle from the vertical it is called a slant engine, chryslers Slant 6 was used in many models in the 1960s and 1970s. Honda also often mounts its straight-four and straight-five engines at a slant, as on the Honda S2000, SAAB initially used the Triumph Slant-4 engine tilted at 45 degrees for the Saab 99, but later versions of the engine were less tilted. Two main factors have led to the recent decline of the straight-six in automotive applications, second, fuel consumption became more important, as cars became smaller and more space-efficient. The engine bay of a small or medium car, typically designed for an inline-four, often does not have room for a straight-six. Straight-6 engines are used in models from BMW, Ford, Jeep, Chevrolet, GMC, Toyota, Suzuki. Some buses and trains with engines have their engines mounted with the row of cylinders horizontal. This differs from an engine because it is essentially an inline engine laid on its side. Underfloor engines for buses and diesel multiple units use this design. Such engines may be based on an upright engine with alterations to make it suitable for horizontal mounting. In aviation, the inline engine is used more broadly. Some straight engines, in the sense, have been produced for aircraft
6. Lancia – Lancia is an Italian automobile manufacturer founded in 1906 by Vincenzo Lancia as Lancia & C. It became part of the Fiat Group in 1969, the current company, the company has a strong rally heritage and is noted for using letters of the Greek alphabet for its model names. Lancia vehicles are no longer sold outside of Italy, and comprise only the Ypsilon supermini range, fabbrica Automobili was founded on 29 November 1906 in Turin by Fiat racing drivers, Vincenzo Lancia and his friend, Claudio Fogolin. The first car manufactured by Lancia was the Tipo 51 or 12 HP and it had a small four-cylinder engine with a power output of 28 hp. In 1910 Lancia components were exported to the United States where they were assembled, in 1915, Lancia also manufactured its first truck, the Jota that continued as a dedicated series. In 1937, Vincenzo died of an attack and both his wife, Adele Miglietti Lancia, and his son, Gianni Lancia, took over control of the company. They persuaded Vittorio Jano to join as an engineer, Jano had already made a name for himself by designing various Alfa Romeo models, including some of its most successful race cars ever such as the 6C, P2 and P3. Lancia is renowned in the world for introducing cars with numerous innovations. These include the Theta of 1913, which was the first European production car to feature a complete system as standard equipment. 1948 saw the first 5 speed gearbox to be fitted to a production car, Lancia premiered the first full-production V6 engine, in the 1950 Aurelia, after earlier industry-leading experiments with V8 and V12 engine configurations. It was also the first manufacturer to produce a V4 engine, other innovations involved the use of independent suspension in production cars and rear transaxles, which were first fitted to the Aurelia and Flaminia range. This drive for innovation, constant quest for excellence, fixation of quality, complex construction processes, with little commonality between the various models, the cost of production continued to increase extensively, while demand did not eventually affecting Lancias viability. Gianni Lancia, an engineer was president of Lancia from 1947 to 1955. In 1956 the Pesenti family took control of Lancia with Carlo Pesenti in charge. Fiat launched a bid in October 1969 which was accepted by Lancia as the company was losing significant sums of money. During the 1970s and 1980s, Lancia had great success in rallying, winning many World Rally Championships, during the 1980s, the company cooperated with Saab Automobile, with the Lancia Delta being sold as the Saab 600 in Sweden. The 1985 Lancia Thema also shared a platform with the Saab 9000, Fiat Croma, during the 1990s, all models were closely related to other Fiat models. Starting from 1 February 2007, Fiats automotive operations were reorganised, Fiat Auto became Fiat Group Automobiles S. p. A
7. Балансировка двигателя – Engine balance refers to those factors in the design, production, engine tuning, maintenance and the operation of an engine that benefit from being balanced. Piston engine balancing is a subject that covers many areas in the design, production, tuning. Internal combustion piston engines, by definition, are devices to transform energy in intermittent combustion into energy in mechanical motion. A slider-crank mechanism is used in creating a reaction on fuel with air. The intermittent energy source combined with the nature of this make the engine naturally vibration-prone. Multi-cylinder configuration and many of the design elements are reflections of the effort to reduce vibrations through the act of balancing. This article is organized in six sections, Items to be balanced lists the elements to establish the basics on the causes of imbalance. Types of vibration lists different kinds of vibration as the effects of imbalance, Primary balance discusses the term Primary balance. Secondary balance explains what Secondary balance is, and how the confusing terminologies Primary and Secondary came into popular use, inherent balance goes into engine balance discussions on various multi-cylinder configurations. Steam locomotives is an introduction to the balancing of 2-cylinder locomotives and includes the hammer effect unique to steam locomotives. There are many factors that can contribute to engine imbalance, the following categories will be used for the purposes of this discussion. In the category descriptions, Phase refers to the timing on the rotation of crankshaft, Plane refers to the location on the rotating axis. Mechanical Static Balance - Static balance refers to the balancing of weight, reciprocating mass - e. g. Piston and connecting rod weight and CG uniformity. Rotating mass - e. g. Crank web weight uniformity and flywheel eccentricity Dynamic Balance - In order for a mass to start moving from rest or change direction, a force is required to accelerate a mass. According to Newtons 3rd law of motion, there will be a force in the opposite direction of equal size. Dynamic balance refers to the balancing of forces and forces due to friction. All accelerations of a mass can be divided into two components in opposite directions and this means one cause of engine vibration usually appears in two opposing directions. In other cases, one side is a deflection of a static part, reciprocating mass - Piston mass needs to be accelerated and decelerated, resisting a smooth rotation of a crankshaft
8. Шестицилиндровые двигатели – A V6 engine is a V engine with six cylinders mounted on the crankshaft in two banks of three cylinders, usually set at either a 60 or 90 degree angle to each other. The V6 is one of the most compact engine configurations, usually ranging from 2.0 L to 4.3 L displacement, shorter than the inline 4, because of its short length, the V6 fits well in the widely used transverse engine front-wheel drive layout. The V6 engine has become widely adopted for medium-sized cars, often as an engine where an inline 4 is standard. Modern V6 engines commonly range in displacement from 2.0 to 4.3 L, though larger and smaller examples have been produced, such as the 1991 Mazda MX3, some of the first V6-powered automobiles were built in 1905 by Marmon. This firm became something of a V-engine specialist, beginning with V2 engines, then V4s, V6s, V8s, and, in the 1930s, Marmon was one of the few automakers of the world to offer a V16-powered automobile. From 1908 to 1913 the Deutz Gasmotoren Fabrik produced benzene electric train sets used a V6 as generator engine. Another V6-powered car was designed in 1918 by Leo Goosen for Buick Chief Engineer Walter L. Marr, only one prototype Buick V6 car was built in 1918, it was long used by the Marr family. The first series-production V6 was introduced by Lancia in 1950 with the Lancia Aurelia model, Lancia sought a smoother and more powerful engine that would fit into an existing narrow engine bay. A Lancia engineer, Francesco De Virgilio, began analyzing the vibration of alternative V-angles for a V6 engine in 1943 and he found that a V6 with its cylinders positioned at a 60° V-angle could be made uniquely smooth-running in comparison with other possible V-angles. There was resistance to his conclusion, because the V6 was a virtually unknown engine type in the 1950s and his design featured four main bearings and six crankpins, resulting in evenly spaced firing intervals and low vibrations. Other manufacturers took note and soon other V6 engines were designed, the use of the sweet spot of 60 degrees V-angle maximized power while minimizing vibration and exterior dimensions of the engine. In short, GMC introduced a compact V6 design at a time when the engine was considered the pinnacle of 6-cylinder design. To save design time and expense, it was much like a V8 that had two cylinders chopped off. This uneven firing caused harmonic vibrations in the train that were perceived as a rough-running engine by the buyers. GM sold the tooling to Kaiser-Jeep in 1967, later, as a result of the 1973 oil crisis. In 1977, Buick introduced a split pin crankshaft to implement a version of this engine in which cylinders fired consistently every 120°. The V6 does not have the inherent freedom from vibration that the inline-six and flat-six have, counterweights on the crankshaft and a counter rotating balance shaft are required to compensate for the first order rocking motions. This causes an end-to-end rocking motion at crankshaft speed in a straight-three engine and this results in an engine which is short, light, and relatively smooth, but too wide for most engine compartments
9. Авиация – Aviation is the practical aspect or art of aeronautics, being the design, development, production, operation and use of aircraft, especially heavier than air aircraft. The word aviation was coined by French writer and former naval officer Gabriel La Landelle in 1863, from the verb avier, itself derived from the Latin word avis and the suffix -ation. The modern age of aviation began with the first untethered human lighter-than-air flight on November 21,1783, the practicality of balloons was limited because they could only travel downwind. It was immediately recognized that a steerable, or dirigible, balloon was required, jean-Pierre Blanchard flew the first human-powered dirigible in 1784 and crossed the English Channel in one in 1785. Rigid airships became the first aircraft to transport passengers and cargo over great distances, the best known aircraft of this type were manufactured by the German Zeppelin company. The most successful Zeppelin was the Graf Zeppelin and it flew over one million miles, including an around-the-world flight in August 1929. However, the dominance of the Zeppelins over the airplanes of that period, the Golden Age of the airships ended on May 6,1937 when the Hindenburg caught fire, killing 36 people. The cause of the Hindenburg accident was blamed on the use of hydrogen instead of helium as the lift gas. An internal investigation by the manufacturer revealed the coating used to protect the material over the frame was highly flammable. Changes to the coating formulation reduced the risk of further Hindenburg type accidents, although there have been periodic initiatives to revive their use, airships have seen only niche application since that time. In 1799 Sir George Cayley set forth the concept of the airplane as a fixed-wing flying machine with separate systems for lift, propulsion. Seven years later, on 14 October 1897, Aders Avion III was tested without success in front of two officials from the French War ministry, the report on the trials was not publicized until 1910, as they had been a military secret. In November 1906 Ader claimed to have made a flight on 14 October 1897. Although widely believed at the time, these claims were later discredited, however, the most widely accepted date is December 17,1903 by the Wright brothers. The Wright brothers were the first to fly in a powered and controlled aircraft, previous flights were gliders or free flight, but the Wright brothers combined both, setting the new standard in aviation records. Aircraft began to transport people and cargo as designs grew larger, the Wright brothers took aloft the first passenger, Charles Furnas, one of their mechanics, on May 14,1908. By the beginning of World War II, many towns and cities had built airports, the war brought many innovations to aviation, including the first jet aircraft and the first liquid-fueled rockets. Manufacturers such as Cessna, Piper, and Beechcraft expanded production to provide aircraft for the new middle-class market
10. Daimler-Benz DB 601 – The Daimler-Benz DB601 was a German aircraft engine built during World War II. It was a liquid-cooled inverted V12, and powered the Messerschmitt Bf 109, the DB601 was basically an improved DB600 with direct fuel injection. The DB 601Aa was licence-built in Japan by Aichi as the Atsuta, by Kawasaki as the Ha-40 and this was designated F4, and by 1931 two prototypes were running on the test bench. These were followed by the improved F4B, which became the prototype for the DB600, in 1933, Daimler-Benz finally received a contract to develop its new engine and to build six examples of the DB600. For the year after, the DB600 was the only German aero engine in the 30-litre class, in total,2281 DB 600s were built. The DB 601A-1 was a development of the DB600 with mechanical fuel injection. Like all DB 601s, it had a 33.9 litre displacement, the first DB 601A-1 prototype, designated as F4E, was test run in 1935, and an order for 150 engines was placed in February 1937. Serial production began in November 1937, and ended in 1943, betriebs und Wartungsvorschrift zum Mercedes-Benz Flugmotor DB601 A u. B -1940 dated operation and maintenance manual for the Daimler-Benz DB 601A and DB 601B aircraft engines DB606 power system CAD-based animation of crankcase/conrod/piston components
wikivisually.com
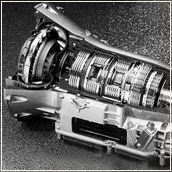
 Двигатель Mercedes V6 Rennmotor
Двигатель Mercedes V6 Rennmotor V-образная схема двигателя — схема расположения цилиндров поршневого двигателя внутреннего сгорания, при которой цилиндры размещаются друг напротив друга под углом от 10° до 120° (наиболее часто 45°, 60° и 90°) в форме латинской буквы «V». В настоящее время в автомобилях чаще всего встречаются конфигурации с 6, 8, в спортивных моделях с 10 и 12 цилиндрами. В мотоциклах — с 2, 4, в спортивных моделях с 5, 6 цилиндрами. В авиационных или корабельных двигателях — с 4, 5, 10, 12 или более цилиндрами. Позволяет сократить линейные размеры мотора по сравнению с рядным расположением цилиндров.
Различные углы развала цилиндров используются в различных двигателях, в зависимости от числа цилиндров. Существуют углы, при которых двигатель работает устойчивее. Очень узкие углы развала цилиндров сочетают в себе преимущества V-образного и рядного двигателей (в первую очередь в виде компактности), так и недостатки; концепция старая, пионером в области её освоения была Lancia, а концерн Volkswagen Group недавно её переработал.
Некоторые конфигурации V-образных двигателей хорошо сбалансированы, в то время как другие работают менее плавно, чем их аналоги среди рядных двигателей. С оптимальным углом развала цилиндров, двигатели V16 имеют ровную работу цилиндров и отличную уравновешенность. Двигатели V10 и V8 могут быть сбалансированы с противовесами на коленчатый вал. Двигатели V12, состоящие из двух рядных шестицилиндровых двигателей, всегда имеют ровную работу цилиндров и отличную уравновешенность независимо от угла развала цилиндров. Другие, такие как V2, V4, V6, V8 и V10, показывают увеличение вибрации и обычно требует балансировки.
Некоторые типы V-образных двигателей были построены перевернутыми, в большинстве своем для авиации. Преимущества включают в себя улучшение видимости из одномоторного самолета и низкий центр тяжести. Примеры включают в себя двигатели Второй мировой войны: немецкие Daimler-Benz DB 601 и двигатели Junkers Jumo.

Обычной практикой считается написание V#, где # обозначает количество цилиндров в двигателе:
pywb-hypothesis.herokuapp.com
Материал из Википедии — свободной энциклопедии
Текущая версия страницы пока не проверялась опытными участниками и может значительно отличаться от версии, проверенной 4 июня 2016; проверки требуют 6 правок.
 Текущая версия страницы пока не проверялась опытными участниками и может значительно отличаться от версии, проверенной 4 июня 2016; проверки требуют 6 правок.
Текущая версия страницы пока не проверялась опытными участниками и может значительно отличаться от версии, проверенной 4 июня 2016; проверки требуют 6 правок.  Двигатель Mercedes V6 Rennmotor
Двигатель Mercedes V6 Rennmotor V-образная схема двигателя — схема расположения цилиндров поршневого двигателя внутреннего сгорания, при которой цилиндры размещаются друг напротив друга под углом от 10° до 120° (наиболее часто 45°, 60° и 90°) в форме латинской буквы «V». В настоящее время в автомобилях чаще всего встречаются конфигурации с 6, 8, в спортивных моделях с 10 и 12 цилиндрами. В мотоциклах — с 2, 4, в спортивных моделях с 5, 6 цилиндрами. В авиационных или корабельных двигателях — с 4, 5, 10, 12 или более цилиндрами. Позволяет сократить линейные размеры мотора по сравнению с рядным расположением цилиндров.
Различные углы развала цилиндров используются в различных двигателях, в зависимости от числа цилиндров. Существуют углы, при которых двигатель работает устойчивее. Очень узкие углы развала цилиндров сочетают в себе преимущества V-образного и рядного двигателей (в первую очередь в виде компактности), так и недостатки; концепция старая, пионером в области её освоения была Lancia, а концерн Volkswagen Group недавно её переработал.
Некоторые конфигурации V-образных двигателей хорошо сбалансированы, в то время как другие работают менее плавно, чем их аналоги среди рядных двигателей. С оптимальным углом развала цилиндров, двигатели V16 имеют ровную работу цилиндров и отличную уравновешенность. Двигатели V10 и V8 могут быть сбалансированы с противовесами на коленчатый вал. Двигатели V12, состоящие из двух рядных шестицилиндровых двигателей, всегда имеют ровную работу цилиндров и отличную уравновешенность независимо от угла развала цилиндров. Другие, такие как V2, V4, V6, V8 и V10, показывают увеличение вибрации и обычно требует балансировки.
Некоторые типы V-образных двигателей были построены перевернутыми, в большинстве своем для авиации. Преимущества включают в себя улучшение видимости из одномоторного самолета и низкий центр тяжести. Примеры включают в себя двигатели Второй мировой войны: немецкие Daimler-Benz DB 601 и двигатели Junkers Jumo.

Обычной практикой считается написание V#, где # обозначает количество цилиндров в двигателе:
pywb-hypothesis.herokuapp.com
Arabic Bulgarian Chinese Croatian Czech Danish Dutch English Estonian Finnish French German Greek Hebrew Hindi Hungarian Icelandic Indonesian Italian Japanese Korean Latvian Lithuanian Malagasy Norwegian Persian Polish Portuguese Romanian Russian Serbian Slovak Slovenian Spanish Swedish Thai Turkish Vietnamese
Arabic Bulgarian Chinese Croatian Czech Danish Dutch English Estonian Finnish French German Greek Hebrew Hindi Hungarian Icelandic Indonesian Italian Japanese Korean Latvian Lithuanian Malagasy Norwegian Persian Polish Portuguese Romanian Russian Serbian Slovak Slovenian Spanish Swedish Thai Turkish Vietnamese
sensagent's content
Webmaster Solution
Alexandria
 A windows (pop-into) of information (full-content of Sensagent) triggered by double-clicking any word on your webpage. Give contextual explanation and translation from your sites !
A windows (pop-into) of information (full-content of Sensagent) triggered by double-clicking any word on your webpage. Give contextual explanation and translation from your sites !
Try hereВ В or В В get the code
SensagentBox
With a SensagentBox, visitors to your site can access reliable information on over 5 million pages provided by Sensagent.com. Choose the design that fits your site.
Business solution
Improve your site content
Add new content to your site from Sensagent by XML.
Crawl products or adds
Get XML access to reach the best products.
Index images and define metadata
Get XML access to fix the meaning of your metadata.
Please, email us to describe your idea.
Lettris
Lettris is a curious tetris-clone game where all the bricks have the same square shape but different content. Each square carries a letter. To make squares disappear and save space for other squares you have to assemble English words (left, right, up, down) from the falling squares.
boggle
 Boggle gives you 3 minutes to find as many words (3 letters or more) as you can in a grid of 16 letters. You can also try the grid of 16 letters. Letters must be adjacent and longer words score better. See if you can get into the grid Hall of Fame !
Boggle gives you 3 minutes to find as many words (3 letters or more) as you can in a grid of 16 letters. You can also try the grid of 16 letters. Letters must be adjacent and longer words score better. See if you can get into the grid Hall of Fame !
English dictionary Main references
Most English definitions are provided by WordNet .English thesaurus is mainly derived from The Integral Dictionary (TID).English Encyclopedia is licensed by Wikipedia (GNU).
Translation
Change the target language to find translations.Tips: browse the semantic fields (see From ideas to words) in two languages to learn more.
В
4694 online visitors
computed in 0.265s
dictionary.sensagent.com