


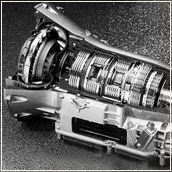




1. Коленчатый вал – A crankshaft—related to crank—is a mechanical part able to perform a conversion between reciprocating motion and rotational motion. In a reciprocating engine, it translates reciprocating motion of the piston into rotational motion, whereas in a reciprocating compressor, a Roman iron crank of yet unknown purpose dating to the 2nd century AD was excavated in Augusta Raurica, Switzerland. The 82.5 cm long piece has fitted to one end a 15 cm long bronze handle, the accompanying inscription is in Greek. The crank and connecting rod mechanisms of the other two archaeologically attested sawmills worked without a gear train, al-Jazari described a crank and connecting rod system in a rotating machine in two of his water-raising machines. His twin-cylinder pump incorporated a crankshaft, though the device was unnecessarily complex, the Italian physician Guido da Vigevano, planning for a new crusade, made illustrations for a paddle boat and war carriages that were propelled by manually turned compound cranks and gear wheels. In Renaissance Italy, the earliest evidence of a crank and connecting-rod is found in the sketch books of Taccola. A sound grasp of the motion involved is demonstrated a little later by Pisanello. One of the drawings of the Anonymous of the Hussite Wars shows a boat with a pair of paddle-wheels at each end turned by men operating compound cranks. Crankshafts were also described by Konrad Kyeser, Leonardo da Vinci and his wind-powered sawmill used a crankshaft to convert a windmills circular motion into a back-and-forward motion powering the saw. Corneliszoon was granted a patent for his crankshaft in 1597, large engines are usually multicylinder to reduce pulsations from individual firing strokes, with more than one piston attached to a complex crankshaft. Many small engines, such as found in mopeds or garden machinery, are single cylinder and use only a single piston. A crankshaft is subjected to stresses, potentially equivalent of several tonnes of force. The crankshaft is connected to the fly-wheel, the block, using bearings on the main journals. An engine loses up to 75% of its energy in the form of friction, noise and vibration in the crankcase. The remaining losses occur in the heat and blow by. The crankshaft has a linear axis about which it rotates, typically with several bearing journals riding on replaceable bearings held in the engine block. As the crankshaft undergoes a great deal of sideways load from each cylinder in an engine, it must be supported by several such bearings. This was a factor in the rise of V8 engines, with their shorter crankshafts, the long crankshafts of the latter suffered from an unacceptable amount of flex when engine designers began using higher compression ratios and higher rotational speeds
2. V-образный двигатель – A V engine, or Vee engine is a common configuration for an internal combustion engine. The cylinders and pistons are aligned, in two planes or banks, so that they appear to be in a V when viewed along the axis of the crankshaft. The Vee configuration generally reduces the engine length, height and weight compared to an equivalent inline configuration. The first V-type engine, a 2-cylinder vee twin, was built in 1889 by Daimler, by 1903 V8 engines were being produced for motor boat racing by the Société Antoinette to designs by Léon Levavasseur, building on experience gained with in-line four-cylinder engines. In 1904, the Putney Motor Works completed a new V12 marine racing engine – the first V12 engine produced for any purpose. Usually, each pair of corresponding pistons from each bank of cylinders share one crankpin on the crankshaft, however, some V-twin engine designs have two-pin cranks, while other V configurations include split crank-pins for more even firing. V-engines are generally more compact than straight engines with cylinders of the same dimensions, various cylinder bank angles of Vee are used in different engines, depending on the number of cylinders, there may be angles that work better than others for stability. Some Vee configurations are well-balanced and smooth, while others are less smoothly running than their equivalent straight counterparts, v8s with crossplane crankshaft can be easily balanced with the use of counterweights only. V12s, being in effect two straight-6 engines married together, are balanced, if the V-angle is 60° for 4-stroke or 30° for 2-stroke. Others, such as the V2, V4, V6, flatplane V8, V10, V14 and V18 engine show increased vibration, certain types of Vee engine have been built as inverted engines, most commonly for aircraft. Advantages include better visibility in an airplane, and lower centre of gravity. Examples include World War II German Daimler-Benz DB601, Junkers Jumo, and Argus Motoren piston engines
3. Рядный двигатель – The straight or inline engine is an internal-combustion engine with all cylinders aligned in one row and having no offset. In-line engines are smaller in overall physical dimensions than designs such as the radial. Straight configurations are simpler than their V-shaped counterparts, although six-cylinder engines are inherently balanced, the four-cylinder models are inherently off balance and rough, unlike 90-degree V fours and horizontally opposed boxer four cylinders. Some manufacturers, including Acura, Audi, Ford, Mercedes-Benz, Volkswagen, the General Motors Atlas family includes straight-four, straight-five, and straight-six engines. Some small cars have three engines. In the 1930s, Duesenberg used a cylinder made from aluminium alloy, with four valves per cylinder. It was thus a selling point for Pontiac to introduce the cheapest straight-eight in 1933, however, following World War II, the straight-eight was supplanted by the lighter and more compact V8 engine, which allowed shorter engine bays to be used in the design. When a straight engine is mounted at an angle from the vertical it is called a slant engine, chryslers Slant 6 was used in many models in the 1960s and 1970s. Honda also often mounts its straight-four and straight-five engines at a slant, as on the Honda S2000, SAAB initially used the Triumph Slant-4 engine tilted at 45 degrees for the Saab 99, but later versions of the engine were less tilted. Two main factors have led to the recent decline of the straight-six in automotive applications, second, fuel consumption became more important, as cars became smaller and more space-efficient. The engine bay of a small or medium car, typically designed for an inline-four, often does not have room for a straight-six. Straight-6 engines are used in models from BMW, Ford, Jeep, Chevrolet, GMC, Toyota, Suzuki. Some buses and trains with engines have their engines mounted with the row of cylinders horizontal. This differs from an engine because it is essentially an inline engine laid on its side. Underfloor engines for buses and diesel multiple units use this design. Such engines may be based on an upright engine with alterations to make it suitable for horizontal mounting. In aviation, the inline engine is used more broadly. Some straight engines, in the sense, have been produced for aircraft
4. Вторая мировая война – World War II, also known as the Second World War, was a global war that lasted from 1939 to 1945, although related conflicts began earlier. It involved the vast majority of the worlds countries—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing alliances, the Allies and the Axis. It was the most widespread war in history, and directly involved more than 100 million people from over 30 countries. Marked by mass deaths of civilians, including the Holocaust and the bombing of industrial and population centres. These made World War II the deadliest conflict in human history, from late 1939 to early 1941, in a series of campaigns and treaties, Germany conquered or controlled much of continental Europe, and formed the Axis alliance with Italy and Japan. Under the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact of August 1939, Germany and the Soviet Union partitioned and annexed territories of their European neighbours, Poland, Finland, Romania and the Baltic states. In December 1941, Japan attacked the United States and European colonies in the Pacific Ocean, and quickly conquered much of the Western Pacific. The Axis advance halted in 1942 when Japan lost the critical Battle of Midway, near Hawaii, in 1944, the Western Allies invaded German-occupied France, while the Soviet Union regained all of its territorial losses and invaded Germany and its allies. During 1944 and 1945 the Japanese suffered major reverses in mainland Asia in South Central China and Burma, while the Allies crippled the Japanese Navy, thus ended the war in Asia, cementing the total victory of the Allies. World War II altered the political alignment and social structure of the world, the United Nations was established to foster international co-operation and prevent future conflicts. The victorious great powers—the United States, the Soviet Union, China, the United Kingdom, the Soviet Union and the United States emerged as rival superpowers, setting the stage for the Cold War, which lasted for the next 46 years. Meanwhile, the influence of European great powers waned, while the decolonisation of Asia, most countries whose industries had been damaged moved towards economic recovery. Political integration, especially in Europe, emerged as an effort to end pre-war enmities, the start of the war in Europe is generally held to be 1 September 1939, beginning with the German invasion of Poland, Britain and France declared war on Germany two days later. The dates for the beginning of war in the Pacific include the start of the Second Sino-Japanese War on 7 July 1937, or even the Japanese invasion of Manchuria on 19 September 1931. Others follow the British historian A. J. P. Taylor, who held that the Sino-Japanese War and war in Europe and its colonies occurred simultaneously and this article uses the conventional dating. Other starting dates sometimes used for World War II include the Italian invasion of Abyssinia on 3 October 1935. The British historian Antony Beevor views the beginning of World War II as the Battles of Khalkhin Gol fought between Japan and the forces of Mongolia and the Soviet Union from May to September 1939, the exact date of the wars end is also not universally agreed upon. It was generally accepted at the time that the war ended with the armistice of 14 August 1945, rather than the formal surrender of Japan
5. Ford – The Ford Motor Company is an American multinational automaker headquartered in Dearborn, Michigan, a suburb of Detroit. It was founded by Henry Ford and incorporated on June 16,1903, the company sells automobiles and commercial vehicles under the Ford brand and most luxury cars under the Lincoln brand. Ford also owns Brazilian SUV manufacturer, Troller, and Australian performance car manufacturer FPV, in the past, it has also produced tractors and automotive components. Ford owns an 8% stake in Aston Martin of the United Kingdom, and it also has a number of joint-ventures, one in China, one in Taiwan, one in Thailand, one in Turkey, and one in Russia. It is listed on the New York Stock Exchange and is controlled by the Ford family, Fords former UK subsidiaries Jaguar and Land Rover, acquired in 1989 and 2000 respectively, were sold to Tata Motors in March 2008. Ford owned the Swedish automaker Volvo from 1999 to 2010, in 2011, Ford discontinued the Mercury brand, under which it had marketed entry-level luxury cars in the United States, Canada, Mexico, and the Middle East since 1938. During the financial crisis at the beginning of the 21st century, it was close to bankruptcy, Ford is the second-largest U. S. -based automaker and the fifth-largest in the world based on 2015 vehicle production. At the end of 2010, Ford was the fifth largest automaker in Europe, Ford is the eighth-ranked overall American-based company in the 2010 Fortune 500 list, based on global revenues in 2009 of $118.3 billion. In 2008, Ford produced 5.532 million automobiles and employed about 213,000 employees at around 90 plants, the company went public in 1956 but the Ford family, through special Class B shares, still retain 40 percent voting rights. The Ford Motor Company was launched in a factory in 1903 with $28,000 in cash from twelve investors, most notably John. During its early years, the company produced just a few cars a day at its factory on Mack Avenue and later its factory on Piquette Avenue in Detroit, Michigan. Groups of two or three men worked on car, assembling it from parts made mostly by supplier companies contracting for Ford. Henry Ford was 39 years old when he founded the Ford Motor Company and it has been in continuous family control for over 100 years and is one of the largest family-controlled companies in the world. The first gasoline powered automobile had been created in 1885 by the German inventor Carl Benz, between 1903 and 1908, Ford produced the Models A, B, C, F, K, N, R, and S. Hundreds or a few thousand of most of these were sold per year, in 1908, Ford introduced the mass-produced Model T, which totalled millions sold over nearly 20 years. In 1927, Ford replaced the T with the Model A, Ford launched the first low-priced car with a V8 engine in 1932. In an attempt to compete with General Motors mid-priced Pontiac, Oldsmobile, Henry Ford purchased the Lincoln Motor Company in 1922, in order to compete with such brands as Cadillac and Packard for the luxury segment of the automobile market. The creation of a laboratory in Dearborn, Michigan in 1951, doing unfettered basic research
6. Ту-85 – The Tupolev Tu-85 was a Soviet prototype strategic bomber based on the Tu-4, an unlicensed reverse engineered copy of the Boeing B-29 Superfortress. It was the development of the B-29 family, being over 50% heavier than its ancestor and had nearly double the range. Only two prototypes were built before the program was canceled in favor of the Tupolev Tu-95 bomber which was faster and had the same range. Neither the Tu-4 nor the Tupolev Tu-80 were true intercontinental strategic bombers as they lacked the range to attack the United States from bases in the Soviet Union and return. The Tu-85 was designed to achieve the range by use of more powerful and fuel-efficient engines, a redesigned wing to increase the lift/drag ratio. Both engines were given turbochargers and power-recovery turbines which converted them into turbo-compound engines, the Shvetsov design was preferred, but was not yet mature enough for use, and the VD-4K was selected. A lot of effort was put into refining the design of the wing in collaboration with TsAGI and it had an aspect ratio of 11.745 and a taper of 2.93 for optimum lift at high-altitudes. The Tu-85 carried 63,600 litres of fuel in 48 flexible tanks, but the Tu-85s tail turret had Argon ranging radar and each of the two bomb bays was enlarged to hold a 9,000 kg FAB-9000 bomb. Construction of the first aircraft began in July 1950 and was completed in September and it first flew on 9 January 1951 and the manufacturers tests lasted until October 1951. On 12 September the first prototype flew 9,020 km with a bombload of 5,000 kg and it was first flown on 28 June 1951 and its trials lasted until November 1951
7. Hawker Typhoon – The Hawker Typhoon, was a British single-seat fighter-bomber, produced by Hawker Aircraft. It was intended to be a medium–high altitude interceptor, as a replacement for the Hawker Hurricane but several problems were encountered. The Typhoon was originally designed to mount twelve.303 inch Browning machine guns and its service introduction in mid-1941 was plagued with problems and for several months the aircraft faced a doubtful future. Through the support of such as Roland Beamont it became established in roles such as night-time intruder. From late 1942 the Typhoon was equipped with bombs and from late 1943 RP-3 ground attack rockets were added to its armoury, with those weapons and its four 20mm Hispano cannon, the Typhoon became one of the Second World Wars most successful ground-attack aircraft. Even before Hurricane production began in March 1937, Sydney Camm had embarked on designing its successor, two preliminary designs were similar and were larger than the Hurricane. These later became known as the N and R, because they were designed for the newly developed Napier Sabre, Hawker submitted these preliminary designs in July 1937 but were advised to wait until a formal specification for a new fighter was issued. The armament fitted was to be twelve.303 inch Browning machine guns with 500 rounds per gun, Camm and his design team started formal development of the designs and construction of prototypes. The wing had a span of 41-foot-7-inch, with an area of 279 sq ft. The airfoil was a NACA22 wing section, with a thickness to chord ratio of 19. 5% at the root tapering to 12% at the tip. The wing possessed great strength, provided plenty of room for fuel tanks. Also incorporated into the wings were inward-retracting landing gear with a wide track of 13 ft 6¾ in. By contemporary standards, the new wing was very thick. The climb rate and performance above that level was considered disappointing. When the Typhoon was dived at speeds of over 500 mph and these compressibility problems led to Camm designing the Typhoon II, later known as the Tempest, which used much thinner wings with a laminar flow airfoil. P5212 also had a small tail-fin, triple exhaust stubs and no wheel doors fitted to the centre-section, on 9 May 1940 the prototype had a mid-air structural failure, at the join between the forward fuselage and rear fuselage, just behind the pilots seat. Philip Lucas could see daylight through the split but instead of bailing out, on 15 May the Minister of Aircraft Production, Lord Beaverbrook, ordered that resources should be concentrated on the production of five main aircraft types. As a result, development of the Typhoon was slowed, production plans were postponed, in the interim between construction of the first and second prototypes, the Air Ministry had given Hawker an instruction to proceed with the construction of 1,000 of the new fighters
8. Н-образный двигатель – An H engine is an engine configuration in which the cylinders are aligned so that if viewed from the front, they appear to be in a vertical or horizontal letter H. An H engine can be viewed as two engines, one atop or beside the other. The two engines each have their own crankshaft, which are geared together at one end for power-take-off. The H configuration allows the building of multi-cylinder engines that are shorter than the alternatives, sometimes delivering advantages on aircraft, the power-to-weight ratio is not as good as simpler configurations employing one crankshaft. There is excellent mechanical balance, especially desirable and otherwise difficult to achieve in a four-cylinder engine, two straight engines can be similarly joined to provide a U engine. Lycoming Lycoming H-2470 H-24 hyper engine Fairey Aviation Fairey Prince -1,500 hp Fairey Monarch - H-242,240 hp Klöckner-Humboldt-Deutz DZ720 - H-32,102.9 litres D. Napier & Son, UK. The British Racing Motors H-16 Formula One engine won the 1966 US Grand Prix with Jim Clark in a Lotus 43, the Brough Superior Golden Dream motorcycle, first shown in 1938. A1,000 cc H-4 design and a few units were produced in early 1939, any development planned was interrupted by World War II and subsequent years of austerity. This was replaced by a flat-four engined prototype at the 1953 show, german firm Konig, who specialised in racing outboard motors, built a few 1000cc H-8s c. 1970s, which were two of their VC500 flat fours mounted one above the other, with the direction of rotation reversed on one of them. Both cylinders at each end of each engine fired at the same time, at least one H-8 found its way into a motorcycle & sidecar racing combo. Subaru produces water-cooled flat-four and flat-six Horizontally-opposed engines that are marketed as h5, the naming scheme refers to engine description, similar to inline engines being named I4 or I6, rather than their appearance front-on
9. Золотник (распределитель) – A piston valve is a device used to control the motion of a fluid along a tube or pipe by means of the linear motion of a piston within a chamber or cylinder. The first piston-valved musical instruments were developed just after the start of the 19th century, the Stölzel valve was an early variety. In the mid 19th century the Vienna valve was an improved design, however most professional musicians preferred rotary valves for quicker, more reliable action, until better designs of piston valves were mass manufactured towards the end of the 19th century. A piston valve can also refer to a 2-way 2-position, pilot-operated spool valve, the term is extremely popular among spud gun enthusiasts who often build homemade piston valves for use in pneumatic cannon. Valves are typically constructed primarily from pipe fittings and machined plastics or metals, the inside of a piston valve contains a piston that blocks the output when the valve is pressurized, and a volume of air behind the piston. When the pressure behind the piston is released the piston is pushed back by the force of the pressure from the input and this allows the valve to be opened by a much smaller pilot valve, with speeds faster than possible with just a manually operated valve. Functionally these types of valves are comparable to quick exhaust valves and this type of piston valve is also sometimes referred to as a back-pressure valve. Angle seat piston valve Early valve designs Why was the valve invented, also includes an e-book library of classic texts on mechanical design and engineering
10. Honda – Honda Motor Co. Ltd. is a Japanese public multinational conglomerate corporation primarily known as a manufacturer of automobiles, aircraft, motorcycles, and power equipment. Honda became the second-largest Japanese automobile manufacturer in 2001, Honda was the eighth largest automobile manufacturer in the world behind General Motors, Volkswagen Group, Toyota, Hyundai Motor Group, Ford, Nissan, and PSA Peugeot Citroën in 2011. Honda was the first Japanese automobile manufacturer to release a luxury brand, Acura. Aside from their automobile and motorcycle businesses, Honda also manufactures garden equipment, marine engines, personal watercraft and power generators. Since 1986, Honda has been involved with artificial intelligence/robotics research and they have also ventured into aerospace with the establishment of GE Honda Aero Engines in 2004 and the Honda HA-420 HondaJet, which began production in 2012. Honda has three joint-ventures in China, in 2013, Honda invested about 5. 7% of its revenues in research and development. Also in 2013, Honda became the first Japanese automaker to be a net exporter from the United States, exporting 108,705 Honda and Acura models, throughout his life, Hondas founder, Soichiro Honda had an interest in automobiles. He worked as a mechanic at the Art Shokai garage, where he tuned cars, in 1937, with financing from his acquaintance Kato Shichirō, Honda founded Tōkai Seiki to make piston rings working out of the Art Shokai garage. After initial failures, Tōkai Seiki won a contract to supply piston rings to Toyota, Honda also aided the war effort by assisting other companies in automating the production of military aircraft propellers. The relationships Honda cultivated with personnel at Toyota, Nakajima Aircraft Company, with a staff of 12 men working in a 16 m2 shack, they built and sold improvised motorized bicycles, using a supply of 500 two-stroke 50 cc Tohatsu war surplus radio generator engines. When the engines ran out, Honda began building their own copy of the Tohatsu engine and this was the Honda A-Type, nicknamed the Bata Bata for the sound the engine made. In 1949, the Honda Technical Research Institute was liquidated for ¥1,000,000, or about US$5,000 today, at about the same time Honda hired engineer Kihachiro Kawashima, and Takeo Fujisawa who provided indispensable business and marketing expertise to complement Soichiro Hondas technical bent. The close partnership between Soichiro Honda and Fujisawa lasted until they stepped down together in October 1973, the first complete motorcycle, with both the frame and engine made by Honda, was the 1949 D-Type, the first Honda to go by the name Dream. Honda Motor Company grew in a time to become the worlds largest manufacturer of motorcycles by 1964. The first production automobile from Honda was the T360 mini pick-up truck, powered by a small 356-cc straight-4 gasoline engine, it was classified under the cheaper Kei car tax bracket. The first production car from Honda was the S500 sports car and its chain-driven rear wheels pointed to Hondas motorcycle origins. Over the next few decades, Honda worked to expand its line and expanded operations. In 1986, Honda introduced the successful Acura brand to the American market in an attempt to ground in the luxury vehicle market
wikivisually.com
V-образная схема двигателя — схема расположения цилиндров поршневого двигателя внутреннего сгорания, при которой цилиндры размещаются друг напротив друга под углом от 10° до 120° (наиболее часто 45°, 60° и 90°) в форме латинской буквы «V». В настоящее время в автомобилях чаще всего встречаются конфигурации с 6, 8, в спортивных моделях с 10 и 12 цилиндрами. В мотоциклах — с 2, 4, в спортивных моделях с 5, 6 цилиндрами. В авиационных или корабельных двигателях — с 4, 5, 10, 12 или более цилиндрами. Позволяет сократить линейные размеры мотора по сравнению с рядным расположением цилиндров.
Различные углы развала цилиндров используются в различных двигателях, в зависимости от числа цилиндров. Существуют углы, при которых двигатель работает устойчивее. Очень узкие углы развала цилиндров сочетают в себе преимущества V-образного и рядного двигателей (в первую очередь в виде компактности), так и недостатки; концепция старая, пионером в области её освоения была Lancia, а концерн Volkswagen Group недавно её переработал.
Некоторые конфигурации V-образных двигателей хорошо сбалансированы, в то время как другие работают менее плавно, чем их аналоги среди рядных двигателей. С оптимальным углом развала цилиндров, двигатели V16 имеют ровную работу цилиндров и отличную уравновешенность. Двигатели V10 и V8 могут быть сбалансированы с противовесами на коленчатый вал. Двигатели V12, состоящие из двух рядных шестицилиндровых двигателей, всегда имеют ровную работу цилиндров и отличную уравновешенность независимо от угла развала цилиндров. Другие, такие как V2, V4, V6, V8 и V10, показывают увеличение вибрации и обычно требует балансировки.
Некоторые типы V-образных двигателей были построены перевернутыми, в большинстве своем для авиации. Преимущества включают в себя улучшение видимости из одномоторного самолета и низкий центр тяжести. Примеры включают в себя двигатели Второй мировой войны: немецкие Daimler-Benz DB 601 и двигатели Junkers Jumo.
Обычной практикой считается написание V#, где # обозначает количество цилиндров в двигателе:
b2b.partcommunity.com
Добрый день. Из всех возможных конфигураций двигателей, ныне больше всего распространены:1. Одноцилиндровый двигатель.2. Однорядный двигатель, где все цилиндры расположены в один ряд.3. U-образный двигатель, представляющей собой два рядных двигателя, коленчатые валы которых механически соединены при помощи цепи или шестерней.4. V-образный двигатель, с двумя рядами цилиндров, расположенных под углом (45° — 90°) друг к другу и работающих на один коленвал.5. Оппозитный двигатель — частный случай V-образного двигателя, где блоки цилиндров расположены под углом 180°.Н-образный двигатель (англ. H engine)5. VR-двигатель — V-образный двигатель с углом развала 15° и накрытый общей головкой блока.6. W-образный двигатель — представляет собой два VR-двигателя соединённых с одним коленвалом.7. Двигатель со встречным движением поршней — с двумя блоками цилиндров, расположенных друг против друга с общей камерой сгорания и отдельными коленчатыми валами.8. Звездообразный двигатель — поршневой двигатель внутреннего сгорания, цилиндры которого расположены радиальными лучами вокруг одного коленчатого вала через равные углы.9. Y-образный двигатель — частный случай звездообразного двигателя, с тремя блоками цилиндров под углом 120°.10. Ротативный двигатель — звездообразный двигатель воздушного охлаждения, основанный на вращении цилиндров (обычно представленных в нечетном количестве) вместе с картером и воздушным винтом вокруг неподвижного коленчатого вала, закреплённого на моторной раме.11. Роторно-поршневой двигатель. Ванкеля.
Москва, Ford Focus ST
blamper.ru