






ЛиАЗ-529260 представляет собой низкопольный автобус среднего класса, предназначенный для работы на пригородных маршрутах со средним и интенсивным пассажиропотоком…
Впервые эта модель, представляющая собой укороченную версию рестайлингового ЛиАЗ-5292, была продемонстрирована общественности в сентябре 2014-го на международном форуме в Нижнем Новгороде, в том же году было запущено ее серийное производство на Ликинском предприятии.

Габаритная длина «пригородного» ЛиАЗ-529260 составляет 10500 мм, его ширина укладывается в 2500 мм (без учета наружных зеркал), высота достигает 2880 мм (с кондиционером – 2938 мм), а межосевое расстояние простирается на 4390 мм.
В «походном» состоянии автобус весит 9280 кг, а его полная масса насчитывает 16200 кг (нагрузка на фронтальную ось не превышает 5580 кг, на заднюю – 10620 кг).

Рабочее место водителя внутри «пригородного» ЛиАЗ-529260 имеет сплошную перегородку (с форточкой и входной дверью), отделяющую его от пассажирского отсека.

Салон машины оснащен 26-ю сиденьями, но с учетом стоячих людей может похвастать 75-ю местами.

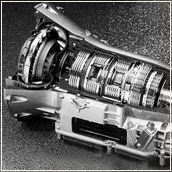
На ЛиАЗ-529260 устанавливается рядный шестицилиндровый дизель ЯМЗ-536111-40 рабочим объемом 6.65 литра (отвечает экологическим нормам «Евро-4») с турбокомпрессором, прямой системой впрыска, 12-ю клапанами, жидкостным охлаждением и интеркулером.Двигатель развивает 275 лошадиных сил при 2300 об/минуту и 1250 Н•м крутящего момента при 1300-1600 об/минуту, а трудится совместно с 6-ступенчатым «автоматом» ZF 6AP-1400B и ведущими задними колесами.
Максимально «пригородный» ЛиАЗ-529260 может набирать скорость 90 км/ч, а потребление горючего у него составляет порядка 35 литров в смешанном режиме передвижения.
Ликинский автобус обладает несущим цельнометаллическим кузовом вагонной компоновки. На обоих мостах автобуса установлены зависимые пневматические подвески с телескопическими амортизаторами: спереди – на двух упругих элементах с парой электронноуправляемых регуляторов положения кузова, сзади – на четырех упругих элементах с двумя механическими регуляторами положения кузова.Машина оснащена рулевой системой типа «винт — шариковая гайка — рейка – сектор» с гидравлическим усилителем управления, электронноуправляемым тормозным комплексом с дисковыми устройствами на всех колесах и ABS, а также топливным баком объемом 248 литров.
На российском рынке приобрести «пригородный» ЛиАЗ-529260 в 2017 году можно по цене от ~7 миллионов рублей.В «базе» автобус имеет: две пневматические двери, ABS, гидроусилитель руля, водительское кресло с пневмоподвеской, автономный отопитель кабины, систему вентиляции, громкую связь с динамиками, люки в крыше и другое оборудование.
Отзывыtruck.ironhorse.ru
Материал из Википедии — свободной энциклопедии
Текущая версия страницы пока не проверялась опытными участниками и может значительно отличаться от версии, проверенной 3 октября 2017; проверки требует 41 правка.
 Текущая версия страницы пока не проверялась опытными участниками и может значительно отличаться от версии, проверенной 3 октября 2017; проверки требует 41 правка. Перейти к навигации Перейти к поиску
Текущая версия страницы пока не проверялась опытными участниками и может значительно отличаться от версии, проверенной 3 октября 2017; проверки требует 41 правка. Перейти к навигации Перейти к поиску | ЛиАЗ-5292 | |
 ЛиАЗ-5292.65 в фирменном окрасе «Московский Транспорт» ЛиАЗ-5292.65 в фирменном окрасе «Московский Транспорт» | |
 ЛиАЗ ЛиАЗ | |
| 2004–настоящее время | |
| не менее 6966 (на апрель 2018)[1] ЛиАЗ-5292.00: 51ЛиАЗ-5292.20: 467ЛиАЗ-5292.21: 1342ЛиАЗ-5292.22: 1892ЛиАЗ-5292.22-01: 132ЛиАЗ-5292.22(рестайлинг для Москвы): 265ЛиАЗ-5292.30: 31ЛиАЗ-5292.56: 16ЛиАЗ-5292.60: 851ЛиАЗ-5292.60 (10,5; 2-2-0): 71ЛиАЗ-5292.60 (10,5; 2-2-2): 54ЛиАЗ-5292.65: 712ЛиАЗ-5292.65 (рестайлинг для Москвы): 491ЛиАЗ-5292.67: 158ЛиАЗ-5292.70: 2ЛиАЗ-5292.71: 189 | |
| 17,7–18,39 | |
ru.bywiki.com
К сожалению, эта модель уникальна в своем ценовом диапазоне или больше не выпускается.
ЛиАЗ 5292, 2004 г
Хочу поведать об эксплуатации рабочего ЛиАЗ 5292. Это один из первых «низкопольников», которые пришли в наш парк. На машинах более позднего прихода многие недостатки устранены, ну а мне что-то приходилось делать самому, а с чем-то смириться. Начну с минусов. Кабина совмещена с салоном (то есть выход на улицу не через отдельную дверь, а через салон). Это худшее решение в автобусе. Во-первых, у многих пассажиров есть привычка зайти и встать у первой створки. Все - при повороте направо я ничего не вижу. Приходится постоянно просить пройти дальше в салон. Ладно, когда есть куда, но бывает, что еду битком и тогда реально при повороте направо еду «на авось», надеясь, что никого не задавлю. Еще минус такой конструкции кабины ЛиАЗ 5292: т.к. первая створка совмещена с салоном, то в дождь или снег, да и просто в мороз, она вся запотевает или обмерзает. И даже если никто не стоит напротив нее, все равно ничего не видно.
Сиденье водителя (на более поздних машинах улучшено) - ужас. Сделала его фирма «мехинструмент». Знаете чем изначально занималась эта фирма? Производством садового инструмента. Вот и делали бы грабли да мотыги, зачем людям жизнь портить своими сиденьями. Мучился я с ним долго: разбирал, смазывал, вкладывал дополнительную набивку. Но конструкция такова, что ничего не поможет. По высоте не регулируется, а по жесткости, если немного мягче сделать, то через несколько кочек весь воздух выходит и сиденье опускается вниз. Руль весь облезает, а голая резина, что остается-собирается катышками и пачкает руки. Приходится надевать чехлы на руль, но и их ненадолго хватает, слезает дерматин, а кожаные мне не встречались. В кабине ЛиАЗ 5292 - отсутствие какого-либо отсека для инструмента и канистры с тосолом и маслом. Единственное место, куда хоть что-то можно положить - аккумуляторный отсек. Отсутствие кондиционера (на более новых машинах стоит). В кабине очень жарко. Она маленькая и очень быстро раскаляется на солнце, сидишь как в парнике. А дверь, как вы помните, выходит не на улицу, открывать бесполезно. Частично решил проблему установкой вентилятора над головой.
Достоинства: надежный.
Недостатки: все в отзыве.
Михаил, Москва
ЛиАЗ 5292, 2005 г
Когда-то работал на ЛиАЗ 5292. Летом от жары спасался, открывая и подвязывая дверь, благо маршрут тогда был не особо напряжённый, народ в кабину не ломился. На счёт видимости - да, если запотеет, не очень удобно, но не смертельно. Зеркало правое плохо видно. Лечится ввариванием в кронштейн 20 см трубы. Нет бардачка. На более поздних ЛиАЗ 5292 был бардачок в салоне между левой передней аркой и кабиной. А мужики у нас самодельные делали такие же. Да и прочие мелочи несущественны. Есть одно большое но - эти автобусы оборудованы механическим ТНВД, а он вечный. Или почти вечный. Не мне тебе рассказывать, как заводятся эфиром или бензином ЛИАЗы выпуска 2010 и позже. 200 тыс. км — умирают электронные форсунки. Я замучался в своё время заводить, наливая бензин через датчик. И это дорогого стоит, когда утром приходишь и заводишь автобус не танцами с бубном, а просто ключом. Эти автобусы с 2010 г. обрели новый двигатель, тоже MAN, но с электронным впрыском. Ресурс форсунок на нашей солярке около 200 тыс. Когда форсунки «кончаются», ЛиАЗ 5292 перестаёт заводиться традиционными способами. Перестаёт тянуть, начинается перерасход, чёрный дым и т.д. Лечение одно — новые форсунки. Но дорого. Когда я работал в парке, одна штука стоила 30000 руб. На фоне политики тотальной экономии моторист пытался эти форсунки ремонтировать сам. В лучшем случае автобус после такого ремонта ходил месяца два-три. Мой рекорд — пять месяцев, но это я лотерейный билет вытянул. А вообще, мне нравилось на такой машине работать, самые теплые воспоминания остались. Очень огорчился, когда заставили НефАЗ получать. С ним, новым, проблем было гораздо больше.
Достоинства: нравилось на такой машине работать.
Недостатки: форсунки.
Дмитрий, Санкт-Петербург
avto-russia.ru
1. Ликинский автобусный завод – For the defunct Czech truck manufacturing company see, LIAZ LiAZ is a bus manufacturing company located in Likino-Dulyovo, Russia. It is now a wholly owned subsidiary of GAZ, specializes in designing and manufacturing buses large and extra large class. The factory was created in 1937 as a processing plant LOZOD. It produced pressed wood products, as well as wood particle boards, in 1944 the factory was renamed to LiMZ and it started producing small machinery like power saws and portable generators. In 1959 the factory started to assemble ZIL-158 passenger buses and it was renamed LiAZ the same year. In 1967 the factory designed and began manufacturing the first bus model of its own named LiAZ-677, the factory produced 194,183 buses of this model in the next 29 years. In 1986 began the production of the new model LiAZ-5256, which today is the most common bus model in Russia. After the collapse of the Soviet Union, LiAZ started to experience difficulties, in 1996 bus manufacturing ceased and the factory declared bankruptcy in 1997. The factory has since been restructured and is now known as Likinskij Avtobusnyj Zavod LLC, in 2000 it was acquired by the RusAvtoProm Corporation, and has been part of the GAZ Group since 2005. LiAZ also manufactured trolleybuses between 2005 and 2012, zIL-158/LiAZ-158, front-engined bus LiAZ-677, front-engined bus with automatic transmission LiAZ-5256, rear-engined bus LiAZ-5292, rear-engined low-floor bus. Buses of this model were used for the Olympic games 2014 in Sochi
2. Caterpillar – Caterpillar is a leading manufacturer of construction and mining equipment, diesel and natural gas engines, industrial gas turbines and diesel-electric locomotives. With more than US$89 billion in assets, Caterpillar was ranked one in its industry. In 2016 Caterpillar was ranked #59 on the Fortune 500 list, Caterpillar stock is a component of the Dow Jones Industrial Average. Caterpillar Inc. traces its origins to the 1925 merger of the Holt Manufacturing Company, Best Tractor Company, creating a new entity, the California-based Caterpillar Tractor Company. In 1986, the company re-organized itself as a Delaware corporation under the current name, Caterpillars headquarters are located in Peoria, Illinois, it announced in January 2017 that over the course of that year it would relocate its headquarters to Chicago. The company also licenses and markets a line of clothing and workwear boots under its Cat / Caterpillar name, Caterpillar machinery is recognizable by its trademark Caterpillar Yellow livery and the CAT logo. Benjamin Holt attempted to fix the problem by increasing the size and width of the wheels up to 7.5 feet tall and 6 feet wide, but this also made the tractors increasingly complex, expensive and difficult to maintain. Another solution considered was to lay a temporary plank road ahead of the tractor, but this was time-consuming, expensive. Holt thought of wrapping the planks around the wheels and he replaced the wheels on a 40 horsepower Holt steamer, No. 77, with a set of wooden tracks bolted to chains, on Thanksgiving Day, November 24,1904, he successfully tested the updated machine plowing the soggy delta land of Roberts Island. Company photographer Charles Clements was reported to have observed that the tractor crawled like a caterpillar, some sources, though, attribute this name to British soldiers in July 1907. Two years later Holt sold his first steam-powered tractor crawlers for US$5,500, each side featured a track frame measured 30 inches high by 42 inches wide and were 9 feet long. The tracks were 3 inches by 4 inches redwood slats, Holt received the first patent for a practical continuous track for use with a tractor on December 7,1907 for his improved Traction Engine. On February 2,1910, Holt opened up a plant in East Peoria, Illinois, there Pliny met farm implement dealer Murray Baker who knew of an empty factory that had been recently built to manufacture farm implements and steam traction engines. On October 25,1909, Pliny Holt purchased the factory, Holt incorporated it as the Holt Caterpillar Company, although he did not trademark the name Caterpillar until August 2,1910. Tractors were built in both Stockton and East Peoria, on January 31,2017, after more than 90 years of being headquartered in Peoria, Illinois, the company announced plans to move their headquarters from Peoria to Chicago, Illinois by the end of 2017. The upper echelon of executives, including newly installed CEO Jim Umpleby, will begin relocating later this year, about 300 employees will work in the new office at an as-yet undecided location once the transition is complete. The changes contributed to $2.3 billion in savings in 2016, Umpleby said that decline is a fundamental reason the companys Board of Directors opted to move global headquarters to an area where the global marketplace is in easier reach
3. Cummins – Dongfeng Motor Corporation is a Chinese state-owned automobile manufacturer headquartered in Wuhan, China. Traditionally one of the Big Three Chinese automakers, Dongfeng is currently in the top four in terms of output along with Changan Motors, FAW Group, in addition to commercial and consumer vehicles, it also manufactures parts and cooperates with foreign companies. Counting six global automakers as partners, it has more Sino-foreign joint ventures than any other Chinese carmaker and these partnerships allow it to produce and sell a variety of foreign-brand products in China including those of Citroën, Honda, Kia, Nissan, Peugeot, and Renault. Other brand names associated with Dongfeng include Fengshen, Infiniti, Luxgen, heavy-duty commercial vehicles and buses are sold under the eponymous Dongfeng brand although c.2015 the Dual Sparrows logo started appearing on consumer products as well. The company was the second-largest Chinese vehicle maker in 2014 by production volume manufacturing over 3.5 million whole vehicles that year, commercial vehicle production that year was higher than all other domestic manufacturers at nearly 450,000. Dongfeng has two listed subsidiaries—Dongfeng Motor Group Co and Dongfeng Automobile Co Ltd. Some sources may refer to the company as Dong Feng, use an acronym like DFM, or use the name in conjunction with others when referring to a subsidiary, joint venture, or other associated enterprise. Known as Second Automobile Works until 1992, Dongfeng, or East Wind in Chinese, was founded in 1969. Its origins lie in a dictate of Chairman Mao Zedong, as part of his Third Front strategy, traditionally manufacturing commercial vehicles, by 2001 these made up about 73% of Dongfengs production. By 2012, that figure had reversed, and 73% of manufactures were passenger cars, however, the percentage of consumer offerings was likely lower as passenger car counts may include microvans, tiny commercial vehicles that are popular in China. Post-1985, further reforms took place that allowed Dongfeng greater autonomy, by the mid-1980s, its assets had tripled from those initially given to it by the state in 1981, and management was desirous of even greater production capacity. But in 1995, the company was experiencing financial difficulties as was the case with many Chinese automobile manufacturers at this time, the situation was still dire in 1998 precipitating a 1999 restructuring of the company. This state owned enterprise has come into conflict with authority at both the national and provincial levels, the Chinese partner in many Sino-foreign joint venture companies, Dongfeng initiated most of these cooperative efforts with foreign firms in the early 2000s. But its first was established in 1992 with French PSA Group, known as Dongfeng Citroën Automobile Company, it was the forerunner to the current Dongfeng Peugeot-Citroën Automobile Limited. By 2003, Dongfeng had established joint ventures with Kia Motors, Honda, as of 2011, it had more Sino-foreign joint ventures than any other Chinese automaker, and the 2013 creation of a partnership with French Renault means it retains this title today. In 2009, it sold 1.9 million vehicles ranking second among domestic automakers, at the 2010 Beijing Auto Show, Dongfeng displayed an electric vehicle concept car, a physical representation of its vow to bring an electric car to market by 2015. In 2010, the company sold 2.72 million units and it reported 1.72 million sales of passenger vehicles that same year. 2011 production figures put the company in place, in terms of production volume, in its home market
4. MAN – MAN SE, formerly MAN AG, is a German mechanical engineering company and parent company of the MAN Group. MAN SE is based in Munich and its primary output is for the automotive industry, particularly heavy trucks. Further activities include the production of engines for various applications, like marine propulsion. MAN supplies trucks, buses, diesel engines and turbomachinery, until September 2012 MAN SE was one of the top 30 companies listed on the German stock exchange. The company celebrated its 250th anniversary in 2008, in 2008, its 51,300 employees generated annual sales of around €15 billion in 120 different countries. The MAN Group currently operates its production output through three main subsidiaries, with each subsidiarys output destined for different locations, MAN Truck & Bus is one of Europes leading commercial vehicle manufacturers. MAN Diesel & Turbo is a leader in large diesel ship engines, stationary engines. MAN Latin America has a position in heavy trucks in Brazil. MAN traces its origins back to 1758, when the St. Antony ironworks commenced operation in Oberhausen, as the first heavy-industry enterprise in the Ruhr region. In 1808, the three ironworks St. Antony, Gute Hoffnung, and Neue Essen merged, to form the Hüttengewerkschaft und Handlung Jacobi, Oberhausen, which was later renamed Gute Hoffnungshütte. In 1840, the German engineer Ludwig Sander founded in Augsburg the first predecessing enterprise of MAN in Southern Germany, reichenbachsche Maschinenfabrik, which was named after the pioneer of printing machines Carl August Reichenbach, and later on the Maschinenfabrik Augsburg. The branch Süddeutsche Brückenbau A. G. was founded when the company in 1859 was awarded the contract for the construction of the bridge over the Rhine at Mainz. In 1898, the companies Maschinenbau-AG Nürnberg and Maschinenfabrik Augsburg AG merged to form Vereinigte Maschinenfabrik Augsburg und Maschinenbaugesellschaft Nürnberg A. G. Augsburg, in 1908, the company was renamed Maschinenfabrik Augsburg Nürnberg AG, or in short, M·A·N. While the focus remained on ore mining and iron production in the Ruhr region. Under the direction of Heinrich von Buz, Maschinenfabrik Augsburg grew from a business of 400 employees into a major enterprise with a workforce of 12,000 by the year 1913. Locomotion, propulsion and steel building were the big topics of this phase, the early predecessors of MAN were responsible for numerous technological innovations. The success of the early MAN entrepreneurs and engineers like Heinrich Gottfried Gerber, was based on a great openness towards new technologies. They constructed the Wuppertal monorail and the first spectacular steel bridges like the Großhesseloher Brücke in Munich in 1857, during 1921, the majority of M. A. N. was taken over by the Gutehoffnungshütte Actienverein für Bergbau und Hüttenbetrieb, Sterkrade
5. Scania – Scania AB, formerly AB Scania-Vabis, is a major Swedish automotive industry manufacturer of commercial vehicles – specifically heavy trucks and buses. It also manufactures engines for motive power of heavy vehicles, marine. Today, Scania has production facilities in Sweden, France, Netherlands, India, Argentina, Brazil, Poland, in addition, there are assembly plants in ten countries in Africa, Asia and Europe. Scanias sales and service organisation and finance companies are worldwide, in 2012, the company employed approximately 42,100 people around the world. Scania was listed on the NASDAQ OMX Stockholm stock exchange from 1996 to 2014, Scanias logo shows a Griffin, from the coat of arms of the province of Scania. AB Scania-Vabis was established in 1911 as the result of a merger between Södertälje-based Vabis and Malmö-based Maskinfabriks-aktiebolaget Scania, Vabis was established as a railway car manufacturer in 1891, while Maskinfabriks-aktiebolaget Scania was established as a bicycle manufacturer in 1900. Both companies had tried their luck at building automobiles, trucks and engines, in 1910, Maskinfabriks-aktiebolaget Scania had succeeded in constructing reliable vehicles, while Vabis was at the brink of closing down. Development and production of engines and light vehicles were set to Södertälje, initially the headquarters were located in Malmö, but in 1912 they were moved to Södertälje. Prince Carl of Sweden owned a 1913 Scania-Vabis 3S, a type which was fitted with in-car buttons so the passenger could communicate with the driver, Scania-Vabis also built two-seat sports cars. For the next few years the companys profits stagnated, with around a third of their orders coming from abroad, the outbreak of the First World War, however, changed the company, with almost all output being diverted to the Swedish Army. By 1916, Scania-Vabis was making enough profit to invest in redeveloping both of their production facilities, following the war, in 1919, Scania decided to focus completely on building trucks, abandoning other outputs including cars and buses. However, they were hurt by the swamping of the market with decommissioned military vehicles from the war, after some economic difficulties in 1921, new capital came from Stockholms Enskilda Bank owned by the Wallenberg family, and Scania-Vabis became a solid and technically, high standing, company. Denmark Towards the end of 1913, the established a subsidiary in Denmark. The following year the first Danish-built car, a four-seater Phaeton, was built at the companys Frederiksberg factory in Copenhagen, in 1914, the factory produced Denmarks first Scania-Vabis truck, and following this developed a V8 engine, one of the first in the world. In 1921, having sold around 175 trucks, and 75 cars, Norway In 1917 an agreement was established with the newly formed Norwegian company Norsk Automobilfabrik A/S about production under license of Scania-Vabis cars and lorries. Production began in 1919, but was ended in 1921 after production of only 77 lorries, during the Second World War Scania produced a variety of military vehicles for the Swedish Army, including Stridsvagn m/41 light tanks produced under licence. During the 1950s, the company expanded its operations into new segments, becoming agents for the Willys Jeep and the Volkswagen Beetle. It also started to become a competitor to Volvo with their new L71 Regent truck which was introduced in 1954
6. Дизельное топливо – Diesel engines have found broad use as a result of higher thermodynamic efficiency and thus fuel efficiency. This is particularly noted where diesel engines are run at part-load, as their air supply is not throttled as in a petrol engine, to distinguish these types, petroleum-derived diesel is increasingly called petrodiesel. Ultra-low-sulfur diesel is a standard for defining diesel fuel with substantially lowered sulfur contents, as of 2016, almost all of the petroleum-based diesel fuel available in UK, Europe and North America is of a ULSD type. In the UK, diesel fuel for use is commonly abbreviated DERV, standing for diesel-engined road vehicle. In Australia diesel fuel is known as distillate, and in Indonesia, it is known as Solar. Diesel fuel originated from experiments conducted by German scientist and inventor Rudolf Diesel for his engine he invented in 1892. Diesel fuel is produced from various sources, the most common being petroleum, other sources include biomass, animal fat, biogas, natural gas, and coal liquefaction. Petroleum diesel, also called petrodiesel, or fossil diesel is the most common type of diesel fuel, synthetic diesel can be produced from any carbonaceous material, including biomass, biogas, natural gas, coal and many others. The raw material is gasified into synthesis gas, which after purification is converted by the Fischer–Tropsch process to a synthetic diesel, the process is typically referred to as biomass-to-liquid, gas-to-liquid or coal-to-liquid, depending on the raw material used. Paraffinic synthetic diesel generally has a content of sulfur and very low aromatics content, reducing unregulated emissions of toxic hydrocarbons, nitrous oxides. Fatty-acid methyl ester, more known as biodiesel, is obtained from vegetable oil or animal fats which have been transesterified with methanol. It can be produced from many types of oils, the most common being rapeseed oil in Europe, methanol can also be replaced with ethanol for the transesterification process, which results in the production of ethyl esters. FAME can be used pure in engines where the manufacturer approves such use, FAME as a fuel is specified in DIN EN14214 and ASTM D6751. Pure biodiesel has an energy content about 5–10% lower than petroleum diesel, the loss in power when using pure biodiesel is 5–7%. As FAME contains low levels of sulfur, the emissions of oxides and sulfates. Use of biodiesel also results in reductions of unburned hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, CO emissions using biodiesel are substantially reduced, on the order of 50% compared to most petrodiesel fuels. The exhaust emissions of particulate matter from biodiesel have been found to be 30% lower than overall particulate matter emissions from petrodiesel, the exhaust emissions of total hydrocarbons are up to 93% lower for biodiesel than diesel fuel. Biodiesel also may reduce risks associated with petroleum diesel
7. Природный газ – It is formed when layers of decomposing plant and animal matter are exposed to intense heat and pressure under the surface of the Earth over millions of years. The energy that the plants originally obtained from the sun is stored in the form of bonds in the gas. Natural gas is a fuel used as a source of energy for heating, cooking. It is also used as fuel for vehicles and as a feedstock in the manufacture of plastics. Natural gas is found in underground rock formations or associated with other hydrocarbon reservoirs in coal beds. Petroleum is another resource and fossil fuel found in proximity to. Most natural gas was created over time by two mechanisms, biogenic and thermogenic, biogenic gas is created by methanogenic organisms in marshes, bogs, landfills, and shallow sediments. Deeper in the earth, at temperature and pressure, thermogenic gas is created from buried organic material. In petroleum production gas is burnt as flare gas. The World Bank estimates that over 150 cubic kilometers of gas are flared or vented annually. Before natural gas can be used as a fuel, most, Natural gas is often informally referred to simply as gas, especially when compared to other energy sources such as oil or coal. However, it is not to be confused with gasoline, especially in North America, Natural gas was used by the Chinese in about 500 BCE. They discovered a way to transport gas seeping from the ground in crude pipelines of bamboo to where it was used to salt water to extract the salt. The worlds first industrial extraction of gas started at Fredonia, New York. By 2009,66000 km³ had been used out of the total 850000 km³ of estimated remaining reserves of natural gas. An annual increase in usage of 2–3% could result in currently recoverable reserves lasting significantly less, unwanted natural gas was a disposal problem in the active oil fields. If there was not a market for natural gas near the wellhead it was expensive to pipe to the end user. In the 19th century and early 20th century, unwanted gas was burned off at oil fields
8. ZF Friedrichshafen AG – ZF Friedrichshafen AG, also known as ZF Group, and commonly abbreviated to ZF, is a German car parts maker headquartered in Friedrichshafen, in the south-west German region of Baden-Württemberg. Specialising in engineering, it is known for its design, research and development. It is a supplier of driveline and chassis technology for cars and commercial vehicles. It is also involved in rail, marine, defence and aviation industries, ZF has 230 production locations in 40 countries with approximately 138,000 employees. The company was founded in 1915 in Friedrichshafen, Germany by Luftschiffbau Zeppelin GmbH, to produce gears for Zeppelins, Zeppelin was unable to otherwise obtain gears for his airships. The German Zahnradfabrik translates to gear factory in English, by 1919, ZF had moved into the automobile market, a move consolidated by the terms of the Treaty of Versailles. Some of the most important milestones that followed,1920, Patent application submitted for the Soden pre-selector transmission,1929, A thriving auto industry warrants the series production of the innovative helical ZF Aphon transmission for cars and commercial vehicles. 1932, Launch of steering systems production under license,1944, On 3 August, the Zahnradfabrik was bombed by the Fifteenth Air Force as a secondary target. As early as 20 September 1942, Albert Speer had warned Hitler of how important the Friedrichshafen tank engine production,1953, Market launch of the first fully synchronised transmission for commercial vehicles worldwide. 1961, Development of an automatic transmission for passenger cars. With series production beginning in 1969, and later proving highly popular, the 1960s sees ZF supplying transmissions to major German automakers as well as Peugeot and Alfa Romeo. 1977, Start of volume production for automatic transmissions for commercial vehicles, worldwide subsidiaries and factories were opened in the 1970s, and the company moved into India and South Korea. 1980s, ZF started operating in Asia in the mid 80s 1984, Majority shareholding gained in Lemförder Metallwaren AG,1986, Start of USA transmission production in Gainesville, Georgia, for pickup trucks. ZF became a supplier to Ford in the 1980s. 1991, The 5HP18 was the first 5-speed automatic transmission for passenger cars, introduced in 1991 on the BMW E36 320i/325i and E345 Series 1994, Development of an automatic transmission system for heavy commercial vehicles. The company expanded into China in the 1990s,1999, World premiere for the first automatic 6-speed transmission. Series production begins in 2001, with the BMW7 Series as the first client, today, ZF produces around one million six-speed automatic transmissions annually. 2001, Acquisition of Mannesmann Sachs AG,2001, Active Roll Stabilization premiere on BMW7 Series 2002, Presentation of the worlds first 4-point link – a newly developed chassis module for trucks and buses
9. Курск – Kursk is a city and the administrative center of Kursk Oblast, Russia, located at the confluence of the Kur, Tuskar, and Seym Rivers. The area around Kursk was the site of a point in the Soviet–German struggle during World War II. Archaeology indicates that the site of Kursk was settled in the 5th or 4th century BCE, the settlement was fortified and included Slavs at least as early as the 8th century CE. The first written record of Kursk is dated 1032 and it was mentioned as one of Severian towns by Prince Igor in The Tale of Igors Campaign, Saddle, brother, your swift steeds. The seat of a principality, Kursk was raided by the Polovtsians in the 12th and 13th centuries. The city was no later than 1283. It was ruled by Grand Duchy of Lithuania between 1360 and 1508, Kursk joined the centralized Russian state in 1508, becoming its southern border province. It was an important center of the trade with Ukraine and hosted an important fair. However, a century later the city re-emerged in a new place, in 1596 a new fortress was built, in 1616 it was garrisoned by over 1,300 soldiers. At the beginning of the 17th century Kursk was repeatedly attacked by Polish-Lithuania, the Crimean Tatars, and the Nogai horde, residents of Oryol and other southern Russian cities were resettled in Kursk. The city developed due to its advantageous position on the shortest route from Moscow to the Crimea. It was raided frequently by the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and Crimean Khanate until the late 17th century and was ruled by the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth between 1611 and 1618 and it was successively part of the Kiev Governorate, Belgorod Governorate, and Kursk Viceroyalty. Town status was granted to Kursk in 1779 and it became the administrative center of Kursk Governorate in 1797. After a fire in 1781 devastated Kursk, a new plan for the city was developed in which a market center would be at the heart of the city, in 1768 the Voskirsensko Ilinskaya Church was built. In 1778 both the Sergiev Cathedral Kazan Cathedral Baroque and Trinity Sergius Cathedral were completed, the city opened its first school for the nobility in 1783. A mens gymnasium was opened in 1808 and a seminary in 1817, a womens gymnasium was opened in 1870. At the beginning of the 20th century Kursk played a dominant role in the industry and in other industries as well, so, in the 1900s. Working conditions in the factories of Kursk were harsh and often resulted in strikes, Kursk workers participated in the general political strike during the 1905 Russian Revolution
10. Лужники (стадион) – Luzhniki Stadium, is a sports stadium in Moscow, Russia. Its total seating capacity is 81,000 seats, all covered and this stadium has the same interior with Gelora Bung Karno Stadium in Indonesia. The stadium is a part of the Luzhniki Olympic Complex, and is located in Khamovniki District of the Central Administrative Okrug of Moscow city, the name Luzhniki derives from the flood meadows in the bend of Moskva River where the stadium was built, translating roughly as The Meadows. In the past its field was used for football games played by PFC CSKA Moscow, Torpedo Moscow and Spartak Moscow. Today it is used as one of the home grounds of the Russian national football team. It is one of the few major European stadia to use an artificial pitch, the pitch is necessary because regular grass pitches cannot withstand the harsh Russian winters and must be replaced at high cost. However, a natural grass pitch was installed for the 2008 UEFA Champions League Final. The stadium is used from time to time for various other sporting events. The stadium is located in Khamovniki District of the Central Administrative Okrug of Moscow city, the name Luzhniki derives from the flood meadows in the bend of Moskva River where the stadium was built, translating roughly as The Meadows. It was necessary to find a large plot of land. The proximity of the river, green mass of clean, fresh air - this circumstance alone mattered to select the area of the city of sports. In addition, Luzhniki is located close to the city center. On December 23,1954, the Government of the USSR adopted a resolution on the construction of a stadium in the Luzhniki area in Moscow. The 1952 Summer Olympics in Helsinki brought the Soviet team 71 medals and top place in the team standings. It was a success, but increased athletic development of the Soviet Union. The proposed complex was to all modern international standards and at the same time serve as a training base for the Olympic team and arena for large domestic. The stadium was built in 1955–56 as the Grand Arena of the Central Lenin Stadium and it was necessary to demolish a whole area of dilapidated buildings. Because the soil was heavily waterlogged, almost the entire area of the future of the complex had to be raised half a meter,10,000 piles were hammered into the ground and dredgers reclaimed about 3 million cubic meters of soil
wikivisually.com
В конце 2013 года Ликинский автобусный завод приступил к производству принципиально новых низкопольных автобусов ЛиАЗ-5292.30 с применением самых передовых технологий. Первые 30 машин были задействованы в транспортном обслуживании Олимпийских и Паралимпийских Зимних Игр в Сочи. В начале марта мы отправились на ЛиАЗ, чтобы познакомиться с новой серийной моделью городского пассажирского автобуса

Ни для кого не секрет, что разработка новой модели автобуса требует больших финансовых затрат. Кроме того, для работы низкопольных автобусов нужна хорошая инфраструктура, и они достаточно дороги, поэтому средние города отдают предпочтение более дешевым моделям. Несмотря на это, внедрение автобуса нового поколения ЛиАЗ-5292.30 в основной поток выпуска продукции главного конвейера Ликинского автобусного завода стало возможным благодаря проведенной модернизации производственной площадки, включая линию катафорезного грунтования, закупке нового сварочного оборудования и лазерного комплекса для заготовительного производства. В общей сложности на эти цели было выделено свыше 120 миллионов рублей. И это не удивительно, ведь на кону домашняя Олимпиада, а модель 5292.30 специально разрабатывалась к Играм.

Вот такое количество приборов над головой водителя в современном городском лайнере
Дебют городского низкопольного автобуса ЛиАЗ-5292.30 состоялся еще в апреле на международном фестивале «Мир автобусов» в подмосковной Коломне. Там же стало известно о подписании контракта на поставку 30 таких машин, которые будут обслуживать городские маршруты в прибрежном кластере Сочи. Осенью стартовало серийное производство и, как известно, первые 30 машин были в срок поставлены для обслуживания зимних Олимпийских и Паралимпийских игр.

Рабочее место водителя проектировалось с учетом требований международных стандартов по эргономике и комфорту
Итак, ЛиАЗ-5292.30 представляет собой глубокую модернизацию серийно выпускаемой низкопольной городской модели. Кузов машины — несущий, цельнометаллический, вагонной компоновки, длиною 12,3 метра. Внешне новинка вышла достаточно удачной. Машина получила новые переднюю и заднюю маски, состоящие из нескольких элементов, что существенно облегчает проведение ремонтных работ, головную оптику Hella, увеличенное панорамное ветровое стекло и большие электронные маршрутоуказатели. При осмотре автобуса обращает на себя внимание доступность практически всех основных и вспомогательных агрегатов, доступ к которым осуществляется через навесные люки, включая крышку моторного отсека. Понравилась компоновка и самого моторного отсека, доступ к узлам двигателя не вызывает нареканий, все компактно, но не плотно. Предусмотрена и автоматическая система пожаротушения отсека, а вот снизу двигатель не имеет никакой защиты.

Справа от водителя клавиши открывания дверей и блок управления АКП
Вход в пассажирский салон осуществляется через три двухстворчатые двери, причем передняя поворотно-распашного, а 2 и 3 — прислонно-сдвижного типа. Низкий уровень пола и отсутствие ступеней делают удобным вход в салон в любую из дверей, а это в свою очередь позволяет упростить ротацию пассажиров на городском маршруте; наличие системы книлинга, наклоняющей автобус в сторону дверей на 7 градусов, только ускорит этот процесс. Кроме того, при необходимости во время посадки можно использовать механическую выдвижную аппарель, которой оборудована средняя дверь машины.

Салон светлый и просторный, с изогнутыми стильными поручнями
Салон вмещает 112 пассажиров, имеет 27 посадочных мест плюс 3 места оборудовано для людей с ограниченными физическими возможностями. Салон автобуса светлый и просторный. Обшивка боковых стенок и потолка выполнена из светло-серого пластика, который не только радует глаз, но и приятен на ощупь. Пассажирские сиденья пластиковые, с мягкими вставками, вполне удобные. То же самое можно сказать про поручни. Для освещения предусмотрены два ряда ламп по всей длине салона. Не обошлось и без новаторских решений, таких как наливной пол. Данная технология используется на ЛиАЗе с 2013 года. Вкратце выглядит это так: с помощью специального оборудования наносится химический состав, который в течение нескольких часов сохнет, в результате образуется нескользкое износостойкое покрытие, которое хорошо моется. Помимо всего прочего, в салоне олимпийского низкопольника дополнительно установлены датчики задымления и камеры видеонаблюдения.

Накопительная площадка с местами для инвалидных колясок и двумя откидными банкетками
За отопление отвечают жидкостные обогреватели, равномерно расположенные по обоим бортам и под пассажирскими креслами по всей длине салона, плюс отопитель в кабине водителя, а также автономный отопитель. Вентиляцию обеспечивают кондиционер, форточки и два люка в крыше.

За тепло в салоне отвечают жидкостные обогреватели под пассажирскими креслами
Рабочее место водителя спроектировано в соответствии с требованиями международных стандартов по комфорту и эргономике, оснащено новой электронной комбинацией приборов и специальным боксом для дополнительного оборудования. Рулевая колонка регулируется по углу наклона и по вылету. Все органы управления расположены в оптимальной зоне досягаемости. Водительское кресло на пневмоподвеске с высокой спинкой и необходимым количеством регулировок вполне комфортное. В правой верхней части кабины появилось внутреннее салонное зеркало, которое гораздо удобнее обычного. Машина, естественно, оборудована цифровым тахографом, системой ГЛОНАСС и системой «Говорящий город», которая позволит слабовидящим и лишенным зрения людям на городских остановках через специальные наушники получить информацию о том, по какому маршруту движется подошедший автобус и открыты ли его двери для посадки.

Новая модификация низкопольного автобуса ЛиАЗ-5292.30 оснащена двигателем Scania DC09 91A стандарта Евро-4. Это 5-цилиндровый рядный дизель объемом 9,2 литра и мощностью 275 л. с. В качестве трансмиссии используется 6-ступенчатая автоматическая коробка передач ZF. Подвеска на машине полностью пневматическая, тормозная система — с дисковыми тормозными механизмами на обеих осях.

Низкопольник имеет систему книлинга и способен присесть на 7 градусов, средняя дверь оборудована механической выдвижной аппарелью
За рулем 12-метрового автобуса каких-то сверхъестественных ощущений не было, все предельно просто и понятно. Порадовало отсутствие необходимости переключения передач, просто переводишь клавишу блока управления автоматической КП в положение Drive, и машина плавно начинает движение. Плавность хода отменная, мелкие неровности дорожного полотна пневматическая подвеска проглатывает так, что перестаешь обращать на них внимание. Достаточно острое рулевое управление прекрасно дополняет неплохая динамика автобуса, звукоизоляция также на уровне. Отличный обзор, как водителю, так и пассажирам, обеспечивают панорамное ветровое стекло и увеличенная площадь бокового остекления.

Двигатель снизу не имеет никакой защиты. Моторный отсек оборудован автоматической системой пожаротушения
В заключение хочется отметить, что низкопольный городской автобус ЛиАЗ-5292.30, принимавший участие в транспортном обслуживании Олимпийских игр в Сочи, заслуживает высокой оценки. Конечно, то высокотехнологичное оборудование, которым он напичкан, может и не пригодиться в повседневной жизни, однако такие вещи, как удобство входа и выхода и комфорт пассажиров, а также высококачественное исполнение салона и рабочего места водителя, позволяют сделать вывод, что модель практически ни в чем не уступает зарубежным аналогам. Остается добавить, что поставки ЛиАЗ-5292.30 уже начались. После работы в Сочи 30 машин отправятся на ПМЖ в Санкт-Петербург, в декабре прошлого года 25 машин было отгружено ГУП «Мосгортранс», при этом заказы постоянно продолжают поступать.
ОБРАТИТЕ ВНИМАНИЕ
УДОБНО
Внутреннее салонное зеркало на практике оказалось гораздо удобнее.

ПРАКТИЧНО
Бачок омывателя ветрового стекла находится за передней маской машины.

ТЕХНИЧЕСКИЕ ХАРАКТЕРИСТИКИ
| Пассажировместимость, чел. | 112 |
| Количество мест для сидения | 27+1 |
| Снаряженная масса, кг | 11 250 |
| Полная масса, кг | 18 000 |
| Габариты (длина/ширина/высота), мм | 12 310/2500/2880 |
| Колесная база, мм | 5960 |
| Объем топливного бака, л | 220 |
| Двигатель: модель | Scania DC09 91A Евро-4 |
| тип | дизельный, рядный, 5-цилиндровый |
| рабочий объем, см3 | 9291 |
| мощность, л.с. при мин-1 | 275 при 1800 |
| крутящий момент, Нм при мин-1 | 1283 при 1200 |
| Коробка передач | автоматическая ZF 6HP504C |
| Подвеска: передняя/задняя | пневматическая |
| Тормоза | дисковые |
| Шины | 275/70R22,5 |
ЦЕНА
Базовая/тестируемого автомобиля, руб. — 7 000 020/8 500 000
СЕРВИС
Заводская гарантия — 1,5 года или 150 тыс. км пробега
Межсервисный пробег, км — 30 000 км
КОНКУРЕНТЫ
МАЗ-203, Volgabus СитиРитм-12, НефАЗ-5299
Плюсы
Просторный салон с удобными креслами, неплохо организовано рабочее место водителя с сиденьем на пневмоподвеске, плавность хода, возможность перевозки пассажиров с ограниченными возможностями.
Минусы
Отсутствие защиты картера двигателя.
5koleso.ru
 | В этой статье не хватает ссылок на источники информации. Информация должна быть проверяема, иначе она может быть поставлена под сомнение и удалена. Вы можете отредактировать эту статью, добавив ссылки на авторитетные источники. Эта отметка установлена 20 февраля 2012. |
| ЛиАЗ-5292 | |
 | |
|
| |
| 2004—настоящее время | |
| 17,7 | |
| 90 км/ч | |
| Низкопольный городской | |
| 12 000 | |
| 2 500 | |
| 2 800 | |
| 5 960 | |
| 3 | |
| Caterpillar 3116, MAN D0836LOh51, MAN D0836LOH56, MAN D0836LOH65, MAN Е0836LOH01 | |
| Voith Diwa D 854.3E, ZF 6HP504C, ZF 6AP1200B | |
| ЛиАЗ-5292 на Викискладе | |
ЛиАЗ-5292 — российский городской низкопольный автобус большого класса производства Ликинского автобусного завода. Предназначен для крупных городов с интенсивным пассажиропотоком. Выпускается с 2004 года.
Первый экземпляр ЛиАЗ-5292.00 был построен и продемонстрирован широкой публике на Московском Автосалоне в 2003 году. Первый отечественный полностью низкопольный автобус на тот момент имел силовой агрегат идентичный ЛиАЗ-5256.25 — Caterpillar-3116, расположенный поперечно, и автоматическую коробку передач фирмы «Voith» модели Diwa D 854.3E. Автобус был оснащен портальными («низкопольными») мостами Rába и рулевым механизмом Csepel A-500.73-3520-00.
Газовая версия ЛиАЗ-5292.00, обладает тем же набором агрегатов, но вместо дизельного двигателя Caterpillar-3116 установлен газовый двигатель Cummins CGe250 30. Существует два экземпляра автобусов этой модификации.
Эта модификация была впервые продемонстрирована на Московском мотор-шоу 2007 года. Она была создана с помощью немецкой компании IVM Automotive с учетом требований ГУП Мосгортранс. Автобусы этой модификации комплектуется двигателями MAN (Евро3), расположенным продольно, портальными («низкопольными») мостами ZF типа AV-132/87и автоматической коробкой передач ZF 6HP504C типа Ecomat. Ведутся работы по привязке двигателя, отвечающего стандартам Евро 4. С середины 2011 года модификация ЛиАЗ-5292.20 выпускается только для регионов РФ.
Дальнейшее развитие ЛиАЗ-5292.20. Основным отличием от предшественника является двигатель MAN D0836 LOH56, отвечающий экологическим нормам Евро-4. Другими отличиями являются другая приборная панель, аналогичная московским ЛиАЗ-6213.20 2009 года выпуска и новый потолок салона, разработанный фирмой КОРА, а также схема окраски экстерьера, аналогичная ЛиАЗ-6213.20 поставки конца 2010 года. Машины, закупаемые "ГУП Мосгортранс" также оснащены точечной головной оптикой фирмы Hella и системой кондиционирования воздуха в пассажирском салоне и кабине водителя. С лета 2011 года, машины данной модификации массово поставляются в автобусные парки Москвы, а с середины 2012 года и в регионы РФ.
Модификация с двигателем MAN D0836 LOH65, отвечающим нормам Евро-5. Первый экземпляр данной модификации был показан на выставке Комтранс-2011 в сентябре 2011 года и затем отправлен на доработку. Уже в САСовской раскраске первый выставочный экземпляр был отправлен в 14-й автобусный парк. Этот экземпляр отличается новой панелью приборов, а также новым интерьером кабины водителя и пластиковыми подиумами и кожухами колесных арок разработки фирмы КОРА. Данная модификация была запущена в серийное производство в декабре 2011 года. Первые серийные автобусы данной модификации имели стандартную заводскую эмблему, и салон идентичный автобусам модификации ЛиАЗ-5292.21. Более поздние автобусы имеют обновленную заводскую эмблему и модернизированный салон с пластиковыми подиумами разработки фирмы КОРА. Автобусы, выпускаемые с лета 2012 года, имеют салон с поручнями жёлтого цвета, цельное лобовое стекло, обрамление лобового маршрутоуказателя черного цвета и изменённый зад - стало больше прорезей для вентиляции двигателя.
Данная модификация автобуса оборудована учебной кабиной в салоне автобуса. Все остальное совпадает с модификацией ЛиАЗ-5292.22.
Модификация с газовым двигателем MAN E0836 LOH01, отвечающим нормам EEV (Евро-5 +) и автоматической трансмиссией нового поколения ZF Ecolife 6AP1200B . Первый экземпляр данной модификации был показан на выставке Busworld-2010 в июле 2010 года. На этом экземпляре был впервые показан новый салон и новый дизайн передней маски кузова для автобусов семейства ЛиАЗ-5292. В 2012 году эта модификация была запущена в серийное производство. С апреля 2012 года автобусы этой модификации оснащаются кондиционерами.
В сентябре 2009 года на московской выставке «Интеравто-2009» была представлена гибридная версия автобуса 5292[1].
В июне 2012 года на выставке Busworld Russia 2012 был представлен опытный электробус ЛиАЗ-6274. Данный электробус оснащен литий-ионными батареями производства компании "Лиотех". Расчетный максимальный запас хода составляет 200 км. [2][3]
| Технические характеристики | |
| Колёсная формула | 4х2 |
| Кузов | Несущий, вагонной компоновки |
| Количество дверей | 3 |
| Ширина дверей | 1 200 |
| Ресурс кузова, лет | 12 |
| Общее число мест (8 чел/м²) | 100 |
| Число мест для сидения | 20-23 |
| Радиус разворота, м | 11,5 |
| Максимальная скорость, км/ч | 90 |
| Контрольный расход топлива, л/100 км | 29 |
| Тормозная система | пневматическая |
| Длина, мм | 11 990 |
| Ширина, мм | 2 500 |
| Высота, мм | 2 880 |
| База, мм | 5 960 |
| Полная масса, кг | 17 700 |
| Высота потолка в салоне | 2 078 |
| Вентиляция | Естественная через люки и форточки, система кондиционирования воздуха (опция) |
| Система отопления | радиаторного типа |
| Мост | ZF-AV132/87, портальный с колесными редукторами |
| Комплектуется двигателями | MAN D0836LOH04/LOH56/LOH65 |
Из-за недостаточной термоизоляции двигательного отсека и плохого распределения воздуха, поступающего через кондиционер (или через узкие форточки), в задней части салона в жаркое время года создаются условия, весьма далёкие от комфортных.
По состоянию на октябрь 2010 года выпущено более 365 автобусов ЛиАЗ-5292 всех модификаций (на 2012 год уже более двух тысяч). Они эксплуатируются в Москве, Курске, Воронеже, Иркутске, Санкт-Петербурге, Астане, а также во Владимирской, Тверской, Курской, Иркутской, Воронежской, Ивановской, Свердловской, Новгородской, Ярославской, Вологодской областях, Краснодарском крае.

Автобусы ЛиАЗ-5292.20 № 09120 и № 09222 недалеко от центрального входа на Стадион «Лужники», г. Москва

Автобус ЛиАЗ-5292.00 АН 993 46 на остановке «Микрорайон Заря», г. Курск

Автобус ЛиАЗ-52922 с двигателем MAN в экспозиции компании «Русские автобусы» на Московском мотор-шоу 2007 года

Опытный автобус ЛиАЗ-5292.22 в экспозиции компании «Русские автобусы» на выставке КОМТРАНС-2011
dic.academic.ru
| 2004–настоящее время | |||||||||||||||
| 5302 на июль 20151 | |||||||||||||||
| 17,7–18,39 | |||||||||||||||
| 9,95–11,25 | |||||||||||||||
| 65–85 | |||||||||||||||
| низкопольный городской | |||||||||||||||
| Евро-3–EEV Евро-4–EEV | |||||||||||||||
| 20–32 | |||||||||||||||
| 105–112 | |||||||||||||||
| 11 990 | |||||||||||||||
| 2 500 | |||||||||||||||
| 2 880 / 3 140 газовый | |||||||||||||||
| 100% | |||||||||||||||
| 5 960 | |||||||||||||||
| 3 2 | |||||||||||||||
| 2-2-2 2-2-0 | |||||||||||||||
| Caterpillar 3116Cummins CGe 250 30 газMAN D0836 LOh51MAN D0836 LOH56MAN D0836 LOH65MAN Е0836 LOH01 газовыйScania DC09 91AЯМЗ-536111 | |||||||||||||||
| дизельное, CNG | |||||||||||||||
| 29 | |||||||||||||||
| Voith Diwa D 8543EZF Ecomat 6 HP 504 CZF EcoLife 6 AP 1400 B | |||||||||||||||
| ЛиАЗ-5292 на Викискладе | |||||||||||||||
| Технические характеристики246 | |
| Колёсная формула | 4х2 |
| Кузов | Несущий, вагонной компоновки |
| Количество дверей | 3 2 |
| Ширина дверей, мм | 2х 1325 + 1х 1225 |
| Ресурс кузова, лет | 10–12 |
| Общее число мест | 105–112 |
| Число мест для сидения | 20–30 |
| Радиус разворота, м | 11,5 |
| Максимальная скорость, км/ч | 65–85 |
| Расход топлива, л/100 км | 45 |
| Тормозная система | Пневматическая, двухконтурная, с ABS |
| Длина, мм | 11 990 |
| Ширина, мм | 2 500 |
| Высота, мм | 2 880 / 3 140 газовый |
| База, мм | 5 960 |
| Полная масса, кг | 17 700 – 18 390 |
| Высота потолка в салоне | 2200…2280 |
| Вентиляция | Естественная через потолочные люки и форточки; принудительная, система кондиционирования воздуха опции |
| Система отопления | Радиаторного типа |
| Задний мост | ZF-AV132/87/6,5, портальный с центральным коническим редуктором |
| Комплектуется двигателями | Caterpillar 3116, Cummins CGe 250 30 газовый, MAN D0836 LOH041, MAN D0836 LOH56, MAN D0836 LOH65, MAN Е0836 LOH01 газовый, Scania DC09 91A, ЯМЗ-5362 |
| В этой статье не хватает ссылок на источники информации Информация должна быть проверяема, иначе она может быть поставлена под сомнение и удаленаВы можете отредактировать эту статью, добавив ссылки на авторитетные источникиЭта отметка установлена 20 февраля 2012 года |
| |||||||||||||||
ЛиАЗ-5292 Информация Видео
ЛиАЗ-5292 Просмотр темы.ЛиАЗ-5292 что, ЛиАЗ-5292 кто, ЛиАЗ-5292 объяснение
There are excerpts from wikipedia on this article and video
www.turkaramamotoru.com